Background:
Aspiration pneumonia (AP) is the most common cause of death in children with neurological impairment who have gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Fundoplications and gastrojejunal feeding tubes (GJT) are frequently employed to prevent AP in this population. It is not known which of these approaches is more effective in preventing AP and/or in improving survival. The purpose of this study was to compare outcomes of children with neurological impairment and GERD following either a first fundoplication or a first GJT.
Methods:
This was a retrospective cohort study. Eligible patients were children with neurological impairment who had either a fundoplication or GJT between January 1997 and December 2005 at a tertiary‐care children's hospital. The main outcomes measures were postprocedure AP‐free survival and mortality. Propensity analyses were used to control for bias in treatment assignment and prognostic imbalances.
Results:
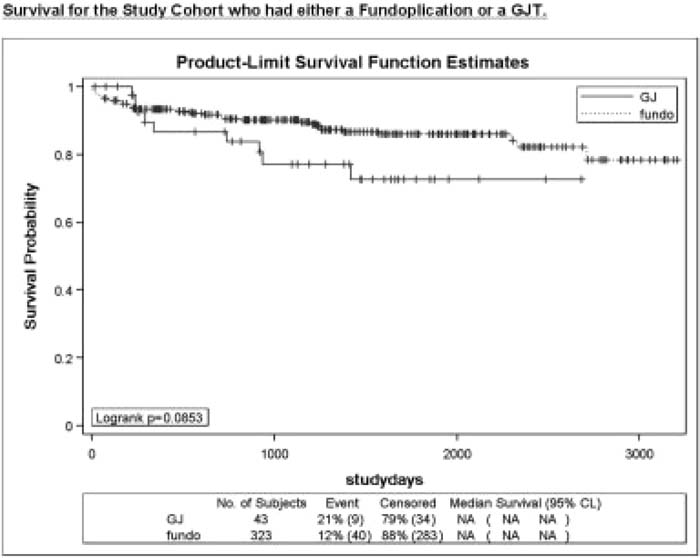
Of the 366 children with neurological impairment and GERD, 43 had a first GJT, and 323 underwent a first fundoplication. Median length of follow‐up was 3.4 years. Children who received a first fundoplication had rates ofAP (hazard ratio 0.71 [0.21‐1.69]) and mortality (hazard ratio 0.49 [0.23‐1.03]) after the procedure similar to those who had a first GJT, when adjusting for treatment assignment using propensity scores.
Conclusions:
AP and mortality are not uncommon after either a first fundoplication or a first GJT for the management of GERD in children with neurological impairment. Neither treatment option is clearly superior in preventing subsequent AP or improving the overall survival of these children. This complex clinical scenario needs to be studied in a multicenter prospective randomized, controlled trial to evaluate definitively whether 1 of these 2 management options is more beneficial.
Author Disclosure:
R. Srivastava, None; E. Downey, None; M. O'Gorman, None; P. Feola, None; M. Samore, None; R. Holobkov, None; M. Mundorff, None; P. Rosenbaum, None; P. Young, None; J. Dean, None.