Background: 22% of the hospitals overall STAR rating is based on readmission reduction for the following disease specific groups: pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, acute myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure. Creating strategies surrounding prevention of readmissions that create workload balance leads to improved ability to manage these patients. The hospitalist medicine, emergency medicine, pulmonary, cardiology, case management, social work and outpatient navigation teams worked symbiotically at our organization to reduce the readmission rate and improve overall quality of care for this patient population.
Purpose: Leveraging the interdisciplinary team to collaboratively manage the STAR CMS patients. Dividing the workload and streamlining the workflow with the utilization of shared responsibility to reduce readmissions within this patient population.
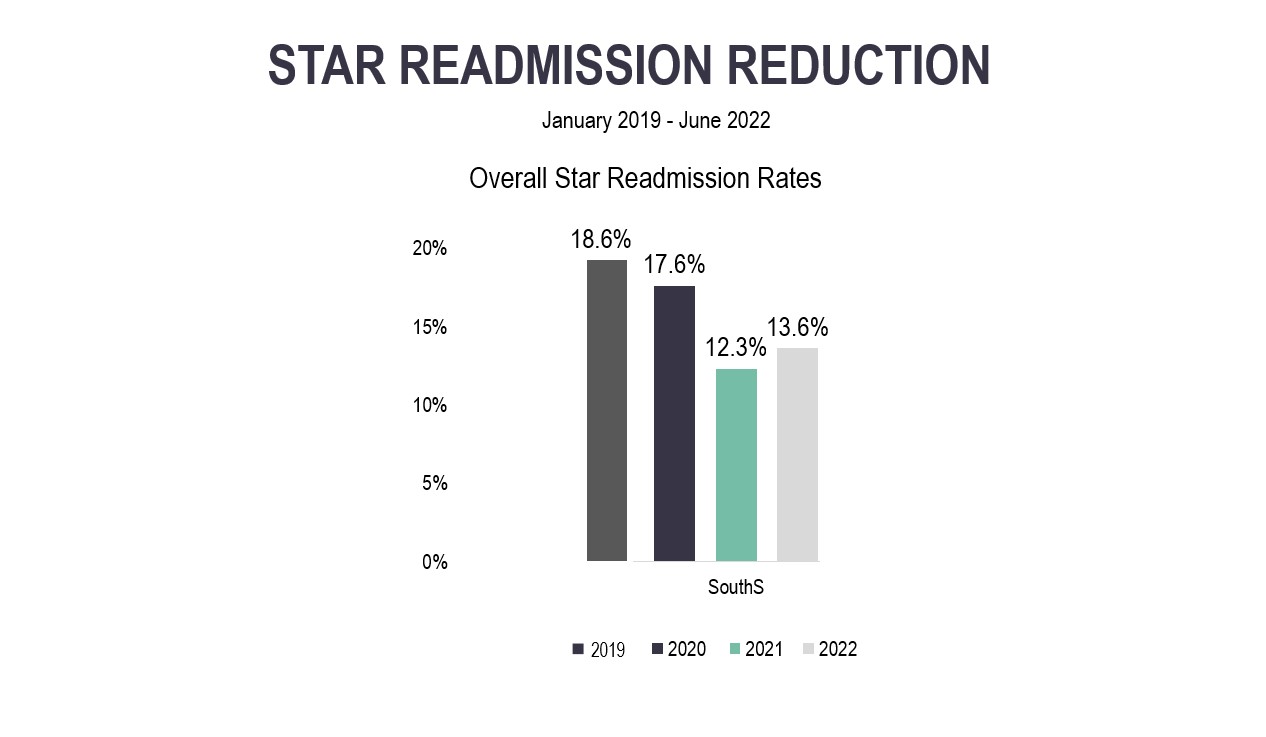
Description: The CMS STAR high risk patient population that are admitted to the hospital are placed on to the STAR CHASE list. This patient list is populated, updated and sent out daily to the above aforementioned parties by the case management team. Each discipline above has specific roles when this list is distributed. The role of the hospitalist/ advanced care practitioner is to engage in an advanced care planning discussion, the case manager will establish a seven-day follow-up appointment with the patients sub specialist and enroll the patient into home care. During transitions of care from the inpatient to the outpatient setting the outpatient navigation team is flagged to ensure the patient is followed in the community. If the patient returns to the emergency room the hospitalist team SWAT these patients with the emergency room providers. This process is directed primarily by the hospitalist team in the day and the emergency medicine team at night. Thorough review of the patient is performed by the emergency room, hospitalist, consultants, outpatient navigator and case management team with the goal to try and manage the patient in the emergency room and transition the patient back outpatient. The organization had a readmission rate of 18.6% in 2019 prior to the initiation of this collaboration and thereafter the readmission percentage continued to down trend and is currently 13.6% in 2022.
Conclusions: An interdisciplinary and collaborative approach in managing patient safety and quality leads to improved outcomes in readmission reduction. With the approach of the team sharing responsibility for the patient there is consistency in the delivery of the care that is being provided and creates a standard that cannot be deviated from.