Background: Medication reconciliation during admission is a critical step in ensuring patient safety and preventing medication errors, particularly as patients often receive new medications during their hospital stays. However, physicians may not always have access to a complete and accurate medication history, which can lead to risks such as drug interactions, incorrect dosing, or adverse events. Inadequate medication reconciliation can also result in prolonged hospitalizations, increased healthcare costs, and potential harm to patients.To address these challenges, this initiative was designed to ensure that patients have the most accurate and up-to-date list of medications by comparing their personal medication records with those in use during hospitalization. This goal will be achieved by standardizing processes, leveraging technology, and fostering multidisciplinary collaboration. The initiative aims to complete medication reconciliation within 24 hours of admission, with a focus on reviewing and documenting any discrepancies, reducing polypharmacy, and ensuring accurate guidance for patient care.The overall aim of this project is to improve compliance with medication reconciliation during admission, increasing the rate from 75% in 2023 to 95% in 2024-2025.
Methods: Collaborating with a multidisciplinary team, we partnered with the clinical pharmacists team to enhance the accuracy of active home medication lists by reviewing admissions in the ED and providing recommendations to residents. Medication reconciliation is completed within 24 hours upon admission. Sources for medication reconciliation include EHR encounters, patients’ personal records, family members, and their pharmacy.Epic specialists simplified the admission medication reconciliation process by consolidating multiple steps into a single screen in Epic, moving outside medication reconciliation to the “sign and hold” tab for easier provider access. To address compliance, providers are notified of incomplete admission medication reconciliation within 24 hours, tracked monthly by auditors through chart review. Education to the health care providers included audiovisual teaching tools, noon conference sessions, one-on-one resident training, and visual aids like posters in workstations, results are supported by regular feedback and monthly performance reviews.
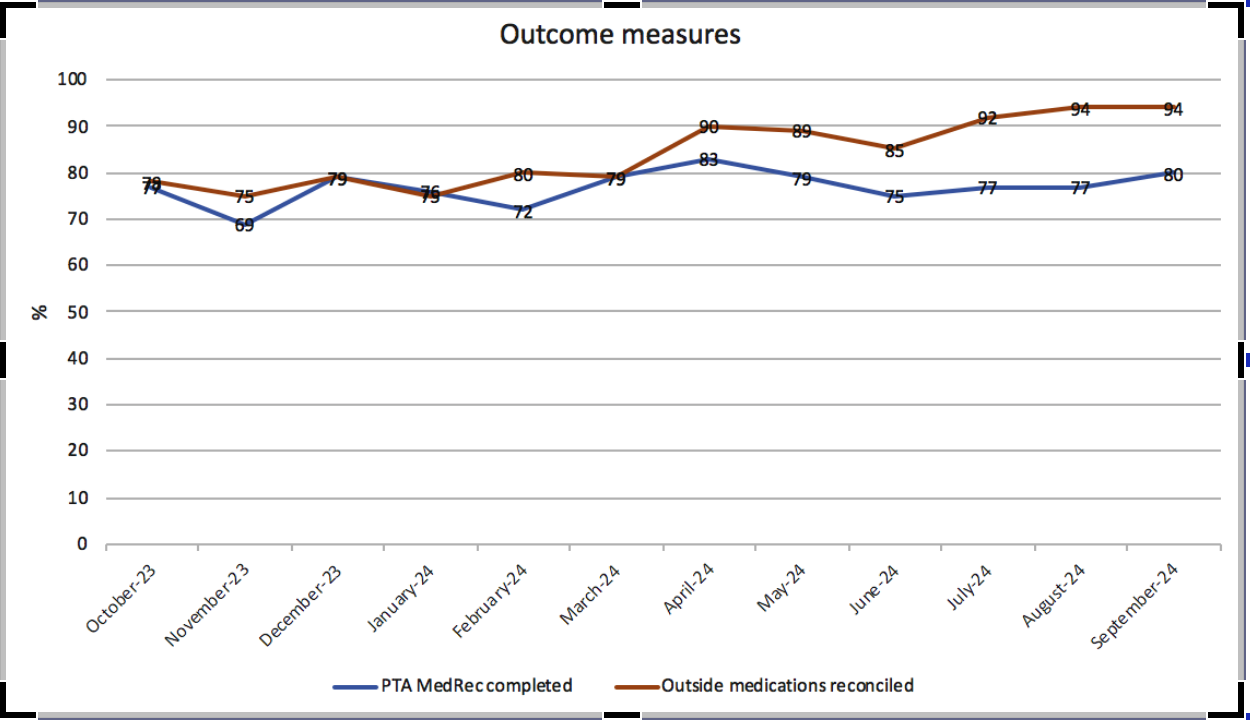
Results: Refer to graph attached.
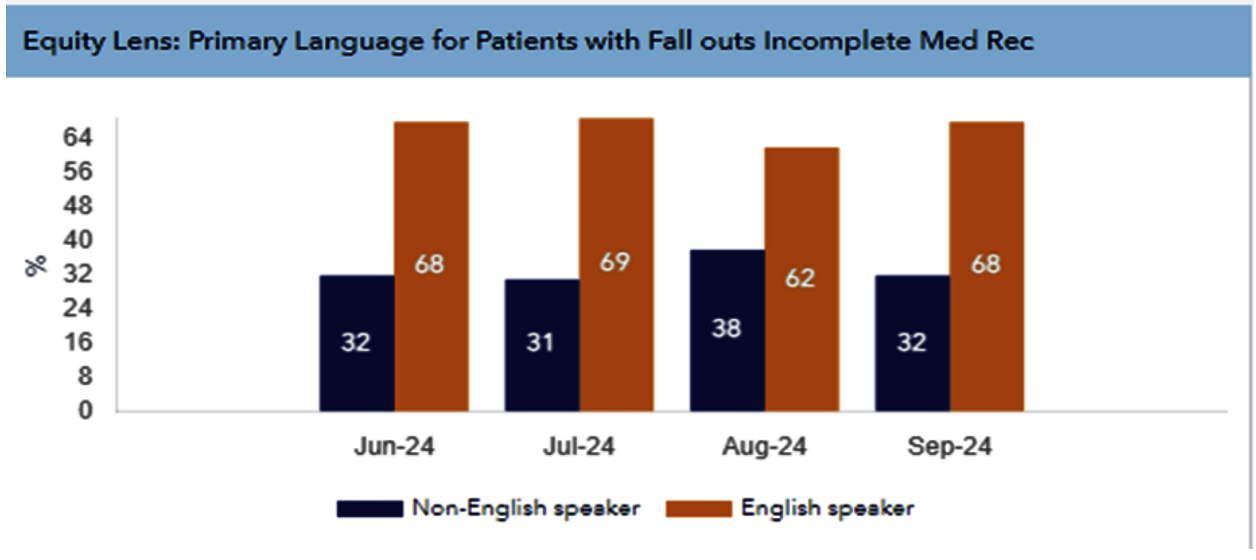
Conclusions: To conclude, admission medication reconciliation is a safety intervention emphasizing the importance of comparing pre-admission with newly prescribed medications. Since the launch of the initiative,our study showed continuous improvement in the rate of reconciliation of outside medication and of prior admission medication. From our equity lens study, language barrier remains as a hindrance to the completion of the process. Interventions to improve compliance of the initiative include simplifying the steps in EPIC to facilitate completion. Health care providers also collaborated with the clinical pharmacist team to improve the rate of accuracy. By completing reconciliation within 24 hours using multiple information sources, we enhance individualized care and minimize errors while continuously rectifying our deficiencies based on audits and feedback to ensure ongoing safety and quality.