Background: Advance care planning (ACP) conversations are essential for aligning care with patients’ values, particularly for high-risk hospitalized patients. However, there are limited tools in hospital medicine to identify and prompt clinicians to engage in ACP conversations effectively. Best Practice Alerts (BPAs) are commonly used in electronic medical records (EMRs) to streamline clinical workflows but have not been widely leveraged to encourage ACP discussions.
Purpose: To design, implement, and evaluate the effectiveness of a non-interruptive BPA that combines a 12-month predictive mortality risk algorithm with a 30-day readmission risk score to encourage advance care planning (ACP) conversations and documentation in hospitalized patients.
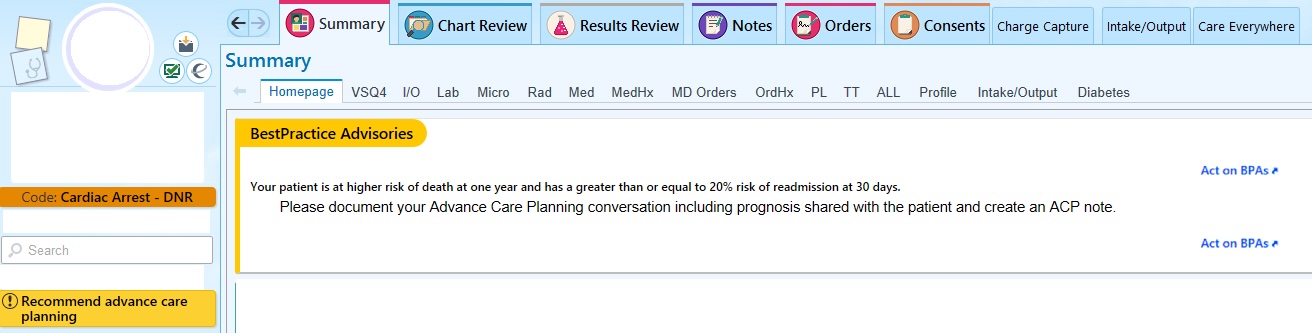
Description: A novel BPA was developed and implemented across our hospital (a tertiary, academic medical center) in October 2022. The BPA criteria included patients who ranked in the top 25th percentile of an in-house developed 12-month predictive mortality algorithm AND had a greater than 20% likelihood of 30-day readmission using EPIC’s Unplanned Readmission algorithm. Patients meeting criteria were randomized 2:1 to either BPA-on or BPA-off groups. In the BPA-on group, the non-interruptive BPA appeared on the patient’s summary page and storyboard (Figure 1). The alert linked directly to the ACP Navigator within the EMR, allowing streamlined documentation of ACP conversations.Between October 2022 and October 2024, there were 6,142 high-risk patient encounters out of 29,478 hospitalizations (21%) on the medicine and oncology services that met the BPA criteria. Following randomization, there were 4,026 encounters in the BPA-on group and 2,116 encounters in the BPA-off group. The BPA-on group demonstrated higher rates of ACP note documentation (54% vs. 50%, p=0.002). Subgroup analysis of house staff teams on the general medicine service revealed similar trends, with higher ACP note documentation in the BPA-on group (40% vs. 35%, p=0.04). No differences were observed in 30-day readmission rates or length of stay between groups.
Conclusions: This novel, non-interruptive BPA represents an innovative approach to integrating ACP into hospital workflows by combining targeted patient identification with a streamlined EMR tool. The BPA enhanced ACP documentation rates while minimizing workflow disruption. This intervention highlights the potential for scalable, sustainable solutions to improve ACP engagement in high-risk hospitalized patients.