Background: There is growing adoption of Observation units as an answer to increasing payment denials in short stay admissions (ranging from 24-72 hours), overcrowding in emergency room, need for inpatient capacity and mismatched resource utilization. There is quite a bit of variation in the type of OBS units like Level I OBS unit- which is usually Emergency Department (ED) managed and protocol based versus Level II OBS unit- managed by Hospital Medicine or other services and non protocol based.
Purpose: Although there is lot of research done around ED managed OBS units, evidence is sparse on the impact of Hospitalist run OBS units at Health systems where there is already a Level I OBS unit run by ED. The patient population, length of stay (LOS), admission rate (OBS to inpatient (IP) conversion) and revisit rate vary quite a bit based on the type of Observation unit. ED based observation unit tend to have defined protocols or pathways based on specific diagnosis with an average LOS ~15 hours. Similar outcomes are not reflected in Level II OBS units due to higher complexity of the patient population and no defined diagnosis based on protocols. In Level II OBS settings, non geographic distribution of patients in the hospital can lead to further increase in LOS.Primary objective of OBS project was to reduce the LOS for OBS patients on Hospital Medicine service. We aimed to achieve this by cohorting all OBS patients admitted under Hospital Medicine service in geographically podded closed unit and providing multidisciplinary team based care.
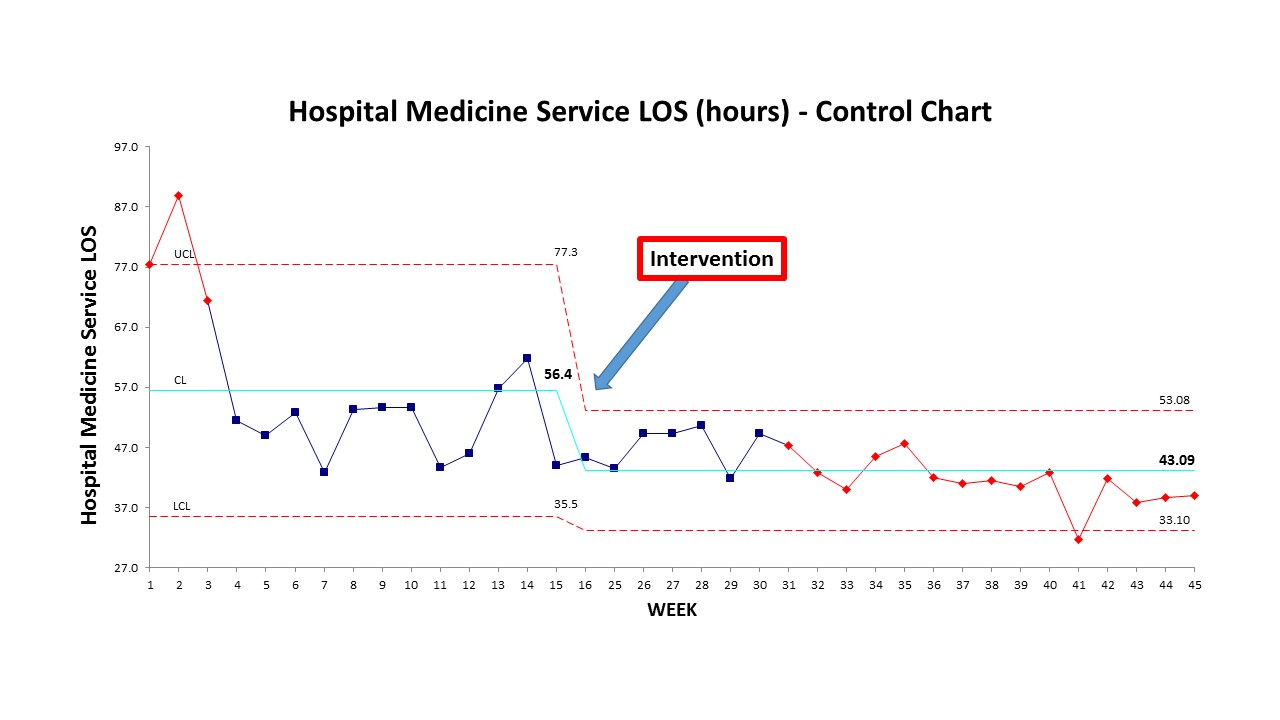
Description: We created a 14 bed OBS unit on a medical-surgical floor in July 2019. Our OBS team consisted of a providers- Attending Physician and Advance Practice Provider (APP), Nursing, Case Manager, Pharmacist. With the help of ED triage team, Patient flow operations and Hospitalist admitting team we were able to capture a majority of patients under Observation patient class to OBS unit. OBS team performed conference room huddle at 10 AM to discuss all the patients on the OBS unit. Another brief huddle at 2 PM was done to discuss new admissions to the unit and potential discharges for the next day. We compared the OBS LOS on Hospital Medicine service before and after the implementation of the OBS project.
Conclusions: Mean LOS decreased to 42.9 hours (95% CI: 40.8-45.1) from 55.6 hours (95% CI: 48.6-62.7) for Hospital Medicine service (p<001). This led to a 12.7 hours of saving on 702 discharges for the period of Jul- Nov, 2019 which accounts to 371.5 bed days saved. Geographic podding and team based care has a positive impact on OBS patients. Further studies should focus on the impact on OBS unit on hospital outcomes like OBS to IP conversions or IP admissions, IP LOS, readmission or revisit rates, patient flow and capacity utilization.