Background: Quality improvement (QI) has been recognized as a core component of medical resident training and progressive engagement with QI is required by the American Council of Graduate Medical Education’s Clinical Learning Environment Review. Prior to 2015, no formal QI education was provided within our internal medicine residency program. This deficiency prompted residency program leadership to collaborate with local QI champions and implement a novel QI curriculum.
Purpose: In an era where healthcare is driven by cost conscious payers focused on outcomes, knowledge of QI fundamentals is an important component of future physician practice. Our team set out to provide trainees with a QI foundation that would serve them for the rest of their careers. Additionally, our team wanted to create an environment for trainees to understand how to work with a multi-disciplinary team to address system issues in a progressive nature.
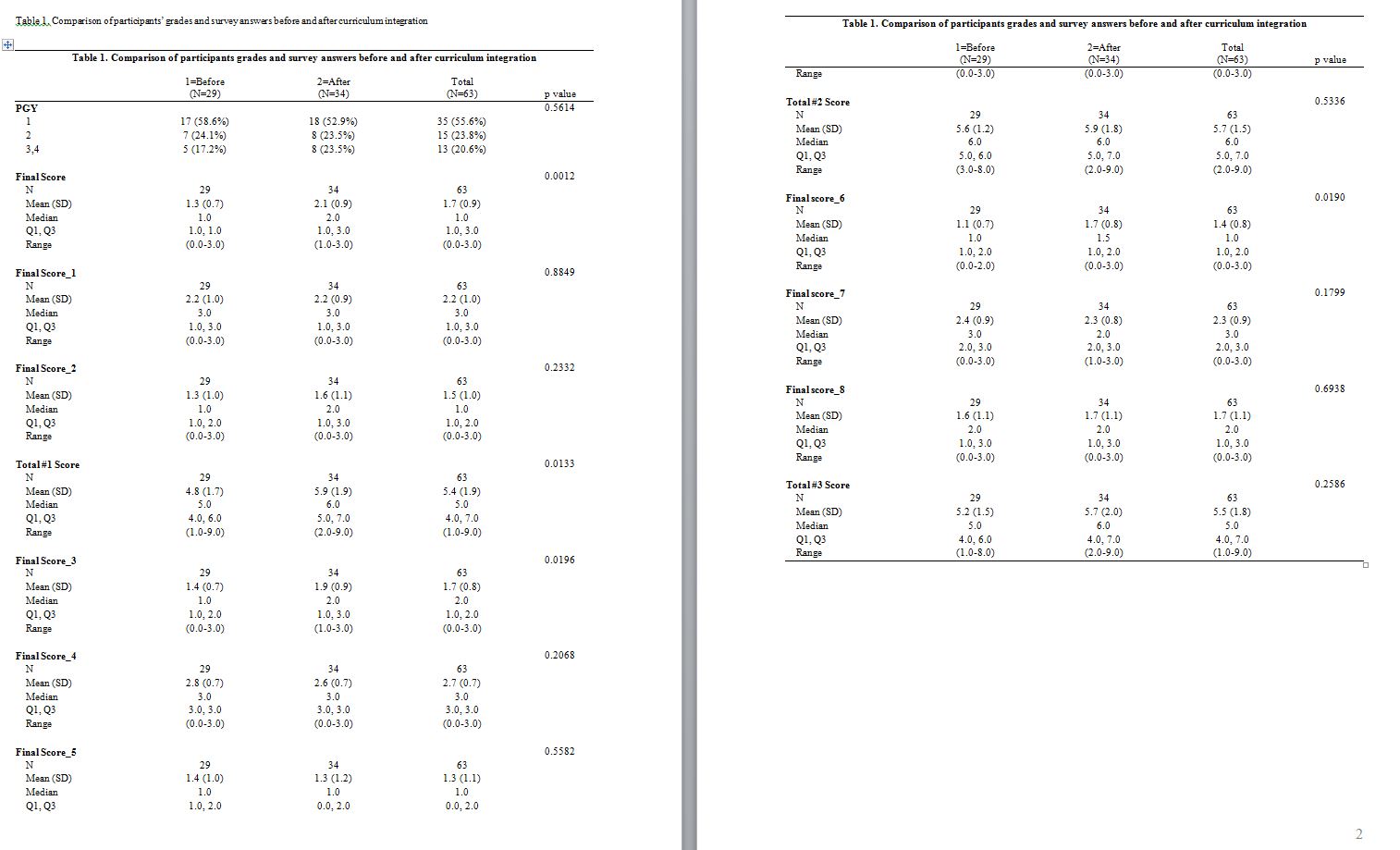
Description: Prior to any interventions being implemented, internal medicine residents were surveyed regarding three unique patient scenarios and their answers were scored utilizing the validated Revised Quality Improvement Knowledge Application Tool (QIKAT-R). Residents were then assigned to one of five unique QI projects for the academic year. Teams consisting of two interns, two second year residents, two third year residents, adjuvant team members, and a faculty mentor with a background in QI would meet monthly and utilize six sigma’s DMAIC process to address a system issue. Biannually the teams reported on their progress and received feedback from the other teams. In the second year of the program a checklist was added to the program and was required to be filled out each meeting to show progression of designated projects. In the third year of implementation we introduced “Quality Thursdays” which included a lecture about QI in the morning and dedicated time in the afternoon for teams to meet and discuss their projects.
Early in the third year of implementation, residents were surveyed again with the same scenarios and data was analyzed utilizing the QIKAT-R tool. 29 out of 45 residents took the survey in 2015 and 34 out of 47 residents took the survey in 2017. The final cumulative mean score for scenarios one, two, and three improved from 4.8. to 5.9 (p-value = 0.0133), 5.6 to 5.9 (p-value = 0.5336), and 5.2 to 5.7 (p-value = 0.2586) respectively. There was no statistically significant difference in resident education level between the two groups.
Conclusions: Integration of a quality improvement curriculum into an internal medicine residency program is necessary at this time in healthcare. Utilizing multidisciplinary team based approaches and annual modifications to expand the breadth of education provided resulted in an increase of quality knowledge as demonstrated by the QIKAT-R tool.