Background: Accurate clinical documentation is essential for capturing patient severity of illness (SOI) and risk of mortality (ROM). These metrics directly influence hospital quality reporting, including rankings like Vizient and metrics such as Observed-to-Expected Mortality (O:E) ratios. Traditional documentation methods rely heavily on manual input, which in busy clinical practices, results in underrepresented patient risk and diminished institutional performance metrics.
Purpose: To evaluate the impact of implementing a health system wide algorithm driven smart phrase with the ability to auto-document diagnoses and plans to improve the capture of risk variables and improve diagnostic precision in provider documentation.
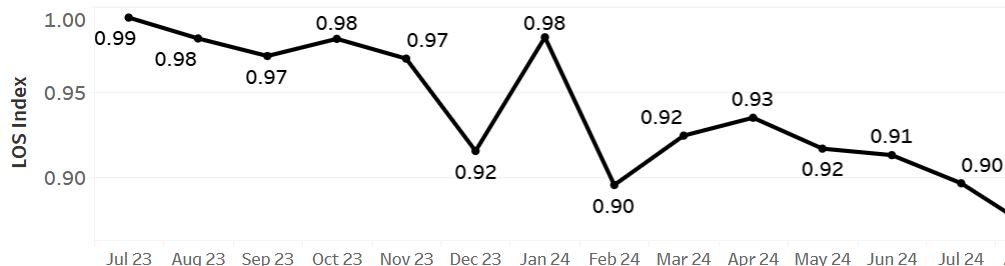
Description: Description:In January 2024, an algorithm-driven smart phrase was seamlessly integrated into provider workflows within the EPIC electronic health record system. This tool was developed by cross-referencing diagnoses commonly targeted by Clinical Documentation Integrity (CDI) queries, Vizient mortality risk variables, and Elixhauser comorbidity variables. Designed to streamline provider documentation, the smart phrase not only enhances efficiency but also ensures the accurate capture of patient risk profiles.Key features of the smart phrase include the ability to auto-document specific diagnoses and associated treatment plans when certain algorithmic criteria are met. For example, if a medication is ordered to address lab abnormalities, such as electrolyte imbalances, the smart phrase will automatically document both the diagnosis and the plan. Supported conditions include: – Electrolyte Imbalances: Hypokalemia, Hyperkalemia, Hypocalcemia, Hypercalcemia, and Hypomagnesemia. – Weight-Based Disorders: Obesity, Morbid Obesity, and Underweight. – Malnutrition: Including auto-documentation of malnutrition severity. This is achieved by extracting and incorporating details from nutritionist assessments, requiring provider validation to finalize documentation.The smart phrase’s integration into provider note templates was supported with targeted education and usage data during the implementation phase to encourage adoption. The primary metric for evaluation was the rate of smart phrase usage, while secondary metrics (lagging indicators) assessed outcomes such as: A. Expected Mortality B. Expected Length of Stay (LOS) C. Query Volume for Lab Abnormalities Results: The implementation resulted in a 45% system-wide usage rate of the smart phrase. This correlated with a 10% improvement in expected mortality rates and a 7% improvement in expected LOS. Additionally, queries related to lab abnormalities were reduced by 20%, reflecting the tool’s impact on documentation completeness and accuracy.
Conclusions: By automating and standardizing documentation practices, this smart phrase tool empowers providers to better capture patient acuity, improve hospital performance metrics, and facilitate high-quality care with minimal effort.