Background: Patients undergoing cardiac surgery are at risk of anemia from blood loss, inflammation, and red blood cell lysis, necessitating blood product utilization and increasing the risk of post-operative complications. RBT-1 (a combination of stannic protoporfin and iron sucrose) is a novel preconditioning drug administered prior to surgery that upregulates anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and iron scavenging pathways. Activation of these pathways, along with the iron content of RBT-1, may improve iron levels, iron utilization, and reduce erythropoietin resistance. A recent phase 2 trial showed that the drug increased cytoprotective protein levels, and improved clinical outcomes. Analyses of anemia incidence, transfusion, and iron usage from the study are presented herein.
Methods: In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 121 patients who were scheduled to undergo non-emergent coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) and/or valve surgery on cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) received one intravenous dose of RBT-1 or placebo between 24 to 48 hours before surgery. Incidence of post-operative anemia, need for blood transfusion, and iron supplementation were recorded. Hemoglobin levels were followed through hospital discharge after surgery.
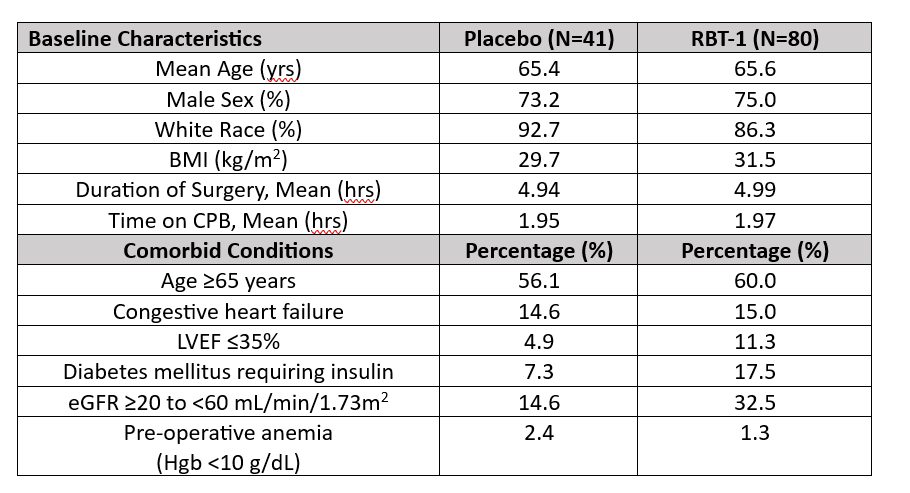
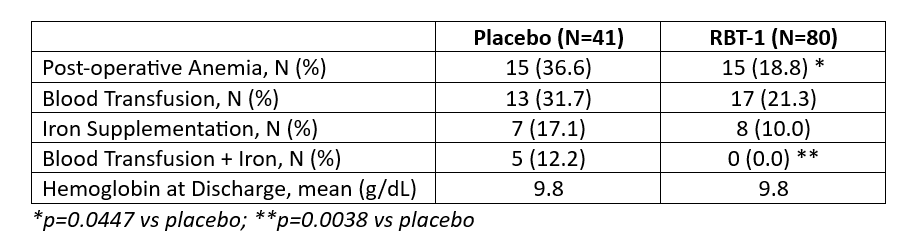
Results: Baseline characteristics and comorbid conditions of the study population are summarized in Table 1. A significant relative risk reduction of 49% in the incidence of post-operative anemia, as reported by the investigators, was observed in response to RBT-1 compared with placebo (p=0.0447). A 33% relative risk reduction in the need for blood transfusion was observed in the RBT-1 group compared with placebo. Similarly, a 42% relative risk reduction in the need for iron supplementation was observed in the RBT-1 group compared with placebo. When comparing all patients who required both blood transfusion and iron, a statistically significant reduction was observed in the RBT-1 group compared with placebo (RBT-1: 0.0% vs Placebo: 12.2%; p=0.0038). Importantly, hemoglobin levels at discharge in patients who received RBT-1 were comparable to those who received placebo despite lesser rates of blood transfusion and iron supplementation (RBT-1: 9.8 g/dL vs Placebo: 9.8 g/dL). Anemia analyses are shown in Table 2.
Conclusions: Treatment with the novel preconditioning drug RBT-1 prior to cardiac surgery may reduce the risk of post-operative anemia and need for blood transfusion and iron supplementation.