Background: Under the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP), a value-based quality initiative by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), the 30-day readmission rate is a critical metric for determining financial penalties for hospitals. However, this metric only accounts for patients readmitted to inpatient units, excluding those who return for observation unit stays or emergency department (ED) visits within 30 days of discharge. Our study aimed to conduct a descriptive analysis to capture 30-day hospital revisits (patients returning to the hospital within 30 days of discharge following an index admission), including inpatient readmissions, Observation Unit stays, and ED visits.
Methods: Data from all hospitalizations (n=76,936) occurring between 2015 and 2023 at a large tertiary care center in Southeastern Wisconsin were analyzed. Eligibility criteria included: 1) Medicare enrollees; 2) an index admission diagnosis of one of the six HRRP-targeted conditions: Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI), Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), Heart Failure, Pneumonia, Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery, or Elective Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty/Total Knee Arthroplasty (THA/TKA); and 3) hospital revisits to inpatient, Observation Unit, or ED.
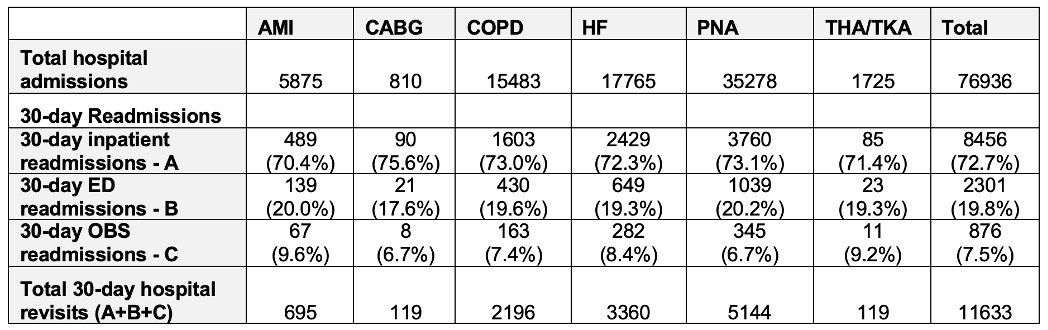
Results: Of all hospitalizations, 11,633 (15%) resulted in 30-day hospital revisits (Table 1). Out of every 100 patients who had 30-day hospital revisits, approximately 8 had Observation Stays, and 20 had ED visits (Table 1). Pneumonia-related revisits accounted for the highest burden (44% of total hospital revisits), followed by Heart Failure (29%) and COPD (19%). Table 2 presents the descriptive statistics for the demographics of patients who had 30-day revisits.
Conclusions: Our study shows that approximately 28% of all 30-day hospital revisits occur through the Observation Unit and ED. The current CMS-HRRP 30-day readmission metric, which only considers inpatient readmissions and excludes Observation Unit stays and ED visits, may miss a significant portion of patients returning to the hospital following an index admission. Further research is needed to investigate the short-term and long-term outcomes of patients with hospital revisits through the Observation Unit and ED compared to those with inpatient readmissions.