Background: Geographical rounding can improve provider to nurse communication as well as between other members of healthcare team resulting in improved efficiency of care. Better communication enables improvement in patient safety and decrease adverse events. Moreover in recent years, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has tied part of hospital’s re-imbursement to patients’ perception of the care provided, and “patient satisfaction” has become an important measure for quality improvement in healthcare . Efficient communication between different healthcare provers is obviously one of the key factors to patient satisfaction. Geographical rounding in specific nursing units offers better opportunity for nurses to work with one particular or less number of healthcare teams rather than multiple teams. This will improve not only nurse-provider communication but also their engagement and help to improve both staff and patient satisfactions.A reduction in length of in-hospital stay (LOS) improved hospital finances. David et al noted reduction in average LOS from 5.06 days to 4.6 days contributing to huge monetary savings for the hospital. In non-academic settings also, geographical rounding was associated with a decreased LOS. Preventable 30-day hospital re-admissions confer enormous cost to healthcare. Improving work environment of healthcare team, team building and Improving communication among team members has the potential to impact re-admission rate and thus savings, by way of improving overall care and clinical outcomes.
Methods: PROCEDURE: . All medicine patients admitted to MEDICINE UNIT 2, regardless of referring area will be taken care of by team Royals.
Comparison of following measures from ‘Medicine unit 2-intervention unit” & Medicine unit 1-control unit, 6 months before and 6 months after intervention.
1- HCAPS score and percentile rank on NRC health reports.
2- Re-admission rate
3- Hospital acquired complications including CAUTI, HCAP, CLABSI, CDAD etc
4- Average length of stay
5- Medicine unit discharge orders entered in EMR
6- Electronic notification of 24 hour prior to discharge
7- Employee engagement: Medical staff, mid-level providers and hospitalist physician survey before and after intervention.
Results: – Patient experience/ NRC health report trends continue to show upward trend in percentile ranking from 62.3 in first quarter to 80.0 in fourth quarter.
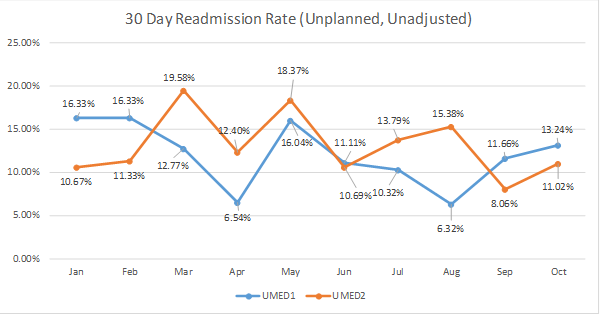
– 30-day re-admission rate was better in intervention unit (11.02%) as compared to control unit (13.24%)
– Average Length of stay (LOS) was equal in both units.
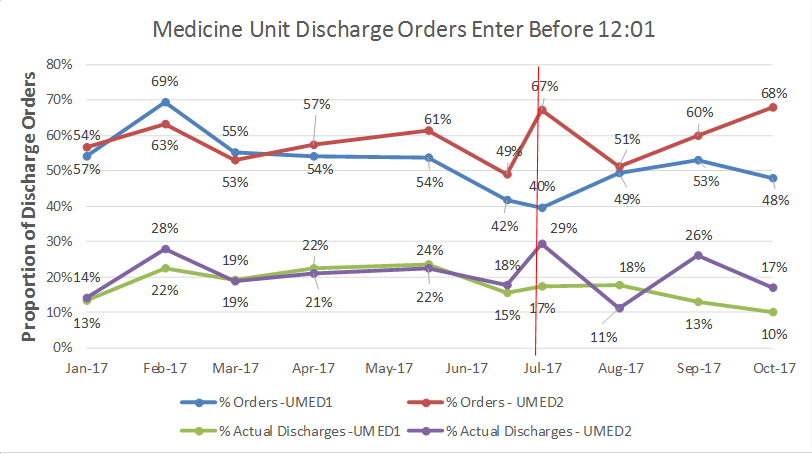
– Medicine unit discharge orders entered in EMR before noon were significantly high (68%) in intervention unit as compared to control unit (48%)
– Electronic notification of 24 hour prior to discharge was significantly high (42%) in intervention unit as compared to control unit (12%)
– Medical staff, mid-level providers and hospitalist physician preferred intervention unit over control unit on study surveys.
Conclusions: Geographical rounding can positively influence patient experience by better communication among healthcare providers, provider availability as well hospital finances by reducing re-admission rate, timely discharges and complications.