Background: Background: SARS-Cov-2 infection (COVID-19) can lead to severe respiratory illness characterized by diffuse pulmonary inflammation similar to what is seen in ARDS. The case series evaluates the additive anti-inflammatory effects of patients that received Tocilizumab, Convalescent Plasma and corticosteroids within 72 hours of hospital admission for critical COVID-19 disease.
Methods: This is a retrospective case series that includes 8 mechanically ventilated patients (5 female and 3 male) with laboratory confirmed COVID-19 admitted with critical disease requiring mechanical ventilation. All patients received tocilizumab, convalescent plasma and methylprednisolone within 72 hours of admission.
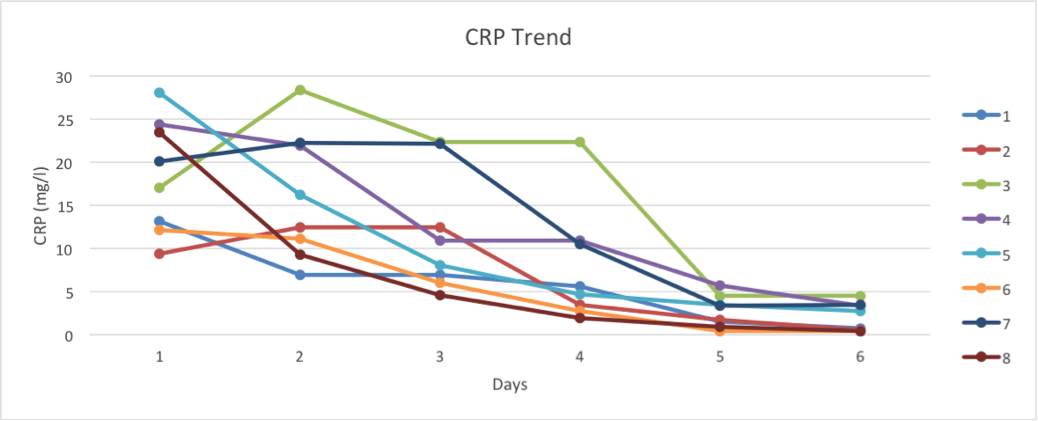
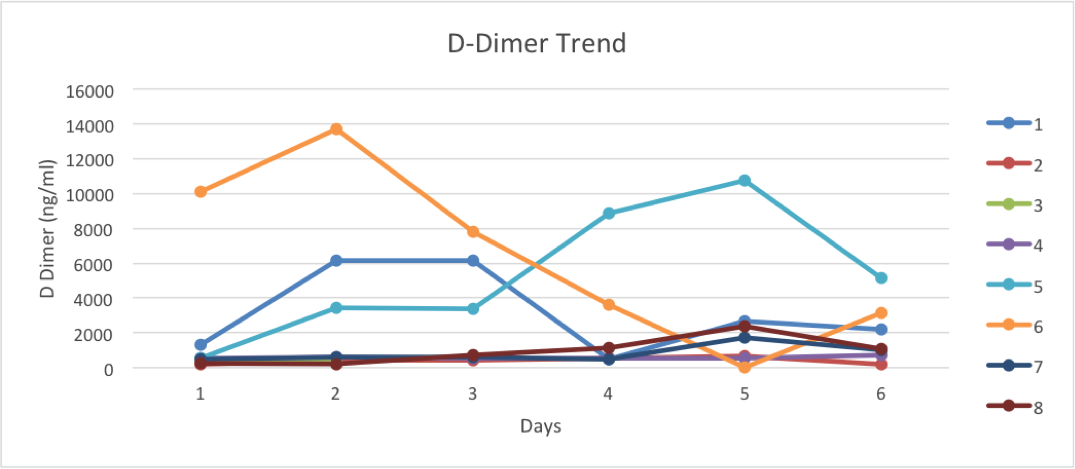
Results: Patient’s ages ranged between 42 and 81 years. The co-morbidities were hypertension (5/8), coronary artery disease (2/8), cerebrovascular disease (1/8), diabetes mellitus type II (3/ 8), Obesity (7/8) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (1/8). Following treatment with tocilizumab and convalescent plasma, inflammatory markers (CRP, D-DImer, LDH, ferritin and white blood cells) were trended. The median difference in the CRP from day one to day six was 17.69 mg/l with IQR (12.53-22.99). Showing a similar decrease in other inflammatory markers, LDH, ferritin and white blood cells further supported this downtrend. However, D-Dimer did not show a decline but showed an uptrend. The median rise in D Dimer from day one to 6 was: 1226 ng/ml with IQR (493-2914). All eight patients were successfully extubated within 16 days and transferred from the critical care unit to a regular medical floor and successfully discharged from the hospital. Mortality was 0 percent at discharge.
Conclusions: Studies suggest the cytokine storm, most importantly Interleukin-6, plays an important role in determining the severity of the disease. Therefore tocilizumab and corticosteroids were used as a potential treatment to dampen the cytokine storm. In order to follow the clinical response to the treatment, the acute inflammatory marker, CRP, was used as an independent factor to predict disease risk. In this preliminary uncontrolled case series of 8 critically ill patients with COVID-19 and ARDS, the addition of tocilizumab to convalescent plasma and corticosteroids showed an improvement in the inflammatory and clinical state. The limited study demonstrates a potential effectiveness of the treatment and further controlled randomized clinical trials are required.