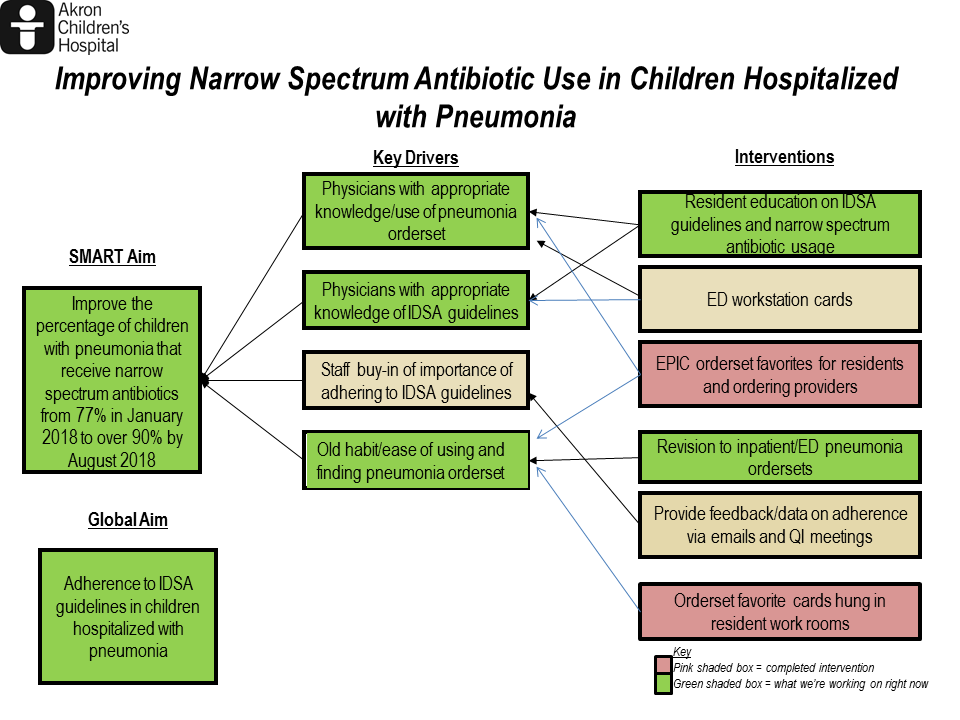
Background: In 2011, the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) published new guidelines on the management of community acquired pneumonia (CAP) in children and recommended use of narrow spectrum antibiotics such as ampicillin or amoxicillin over broader spectrum antibiotics such as ceftriaxone. Many studies have shown that these guidelines have been adopted with varying success across the U.S. At Akron Children’s Hospital, children receive narrow spectrum antibiotics for CAP approximately 77% of the time. This quality improvement project aims to increase the percentage of children receiving narrow spectrum antibiotics from 77% in January 2018 to over 90% by August 2018.
Methods: Using the Model for Improvement we implemented multiple PDSA cycles to increase adherence to IDSA guideline recommendations for antibiotic therapy in children with CAP. We focused on four key drivers to implement educational strategies as well as made modifications to the electronic medical record (EMR) that would enhance narrow spectrum antibiotic use (Figure 1). The charts of patients with CAP were reviewed weekly to determine the percent of children receiving narrow spectrum antibiotics and changes were tracked over time via run charts.
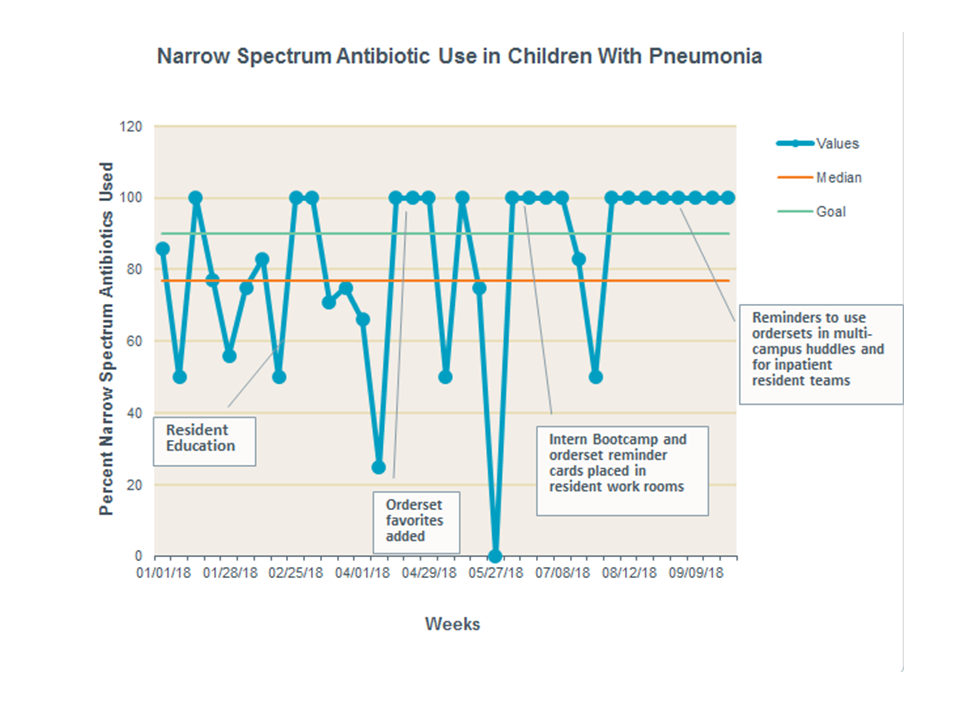
Results: Prescription of narrow spectrum antibiotics increased from 77% to over 90% after education and modifications to the EMR were instituted (Figure 2). Results were sustained for two months.
Conclusions: Modification of the EMR coupled with education can successfully promote antimicrobial stewardship and adherence to national guidelines. This methodology can be broadened to include other conditions besides pneumonia and can be used to promote antimicrobial stewardship in other diseases where therapy guidelines exist.