Background: A discharge summary serves as a crucial means of communication between inpatient and outpatient providers. Appropriate transitions of care rely on updates to patient problems, diagnostics, treatment history, and discharge plans. Many studies have identified lacking components in discharge summaries that may lead to poor medical management.In an effort to improve patient transitions of care, many healthcare institutions have surveyed their general practitioners in order to identify the key components of a high-quality discharge summary. A literature review nets over thirty items as potentially important, far more than the mere six outlined by the Joint Commission on the Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations. The most consistently identified items include discharge diagnoses, management plans/follow-up information, discharge medications, and diagnostics.Several interventions for improving discharge summaries by medical residents have been studied. These include didactic curricula, interactive workshops, or combinations of both. While these interventions have demonstrated significant improvement in the quality of discharge summaries, they used different tools and thus cannot be compared to one another. These tools were developed based on Joint Commission standards, consensus recommendations from other guideline-forming healthcare entities, and previously published or newly attained results from physician surveys.
Purpose: To identify which components of discharge summaries are most valued by primary care providers among the Tulane Internal Medicine network and develop an intervention to improve resident discharge communication to those providers.
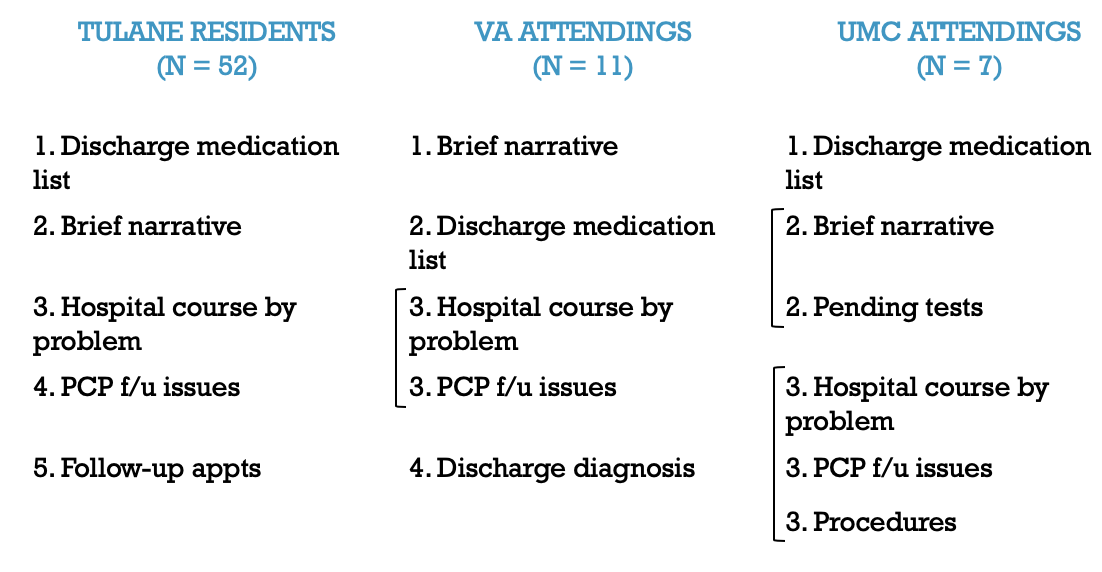
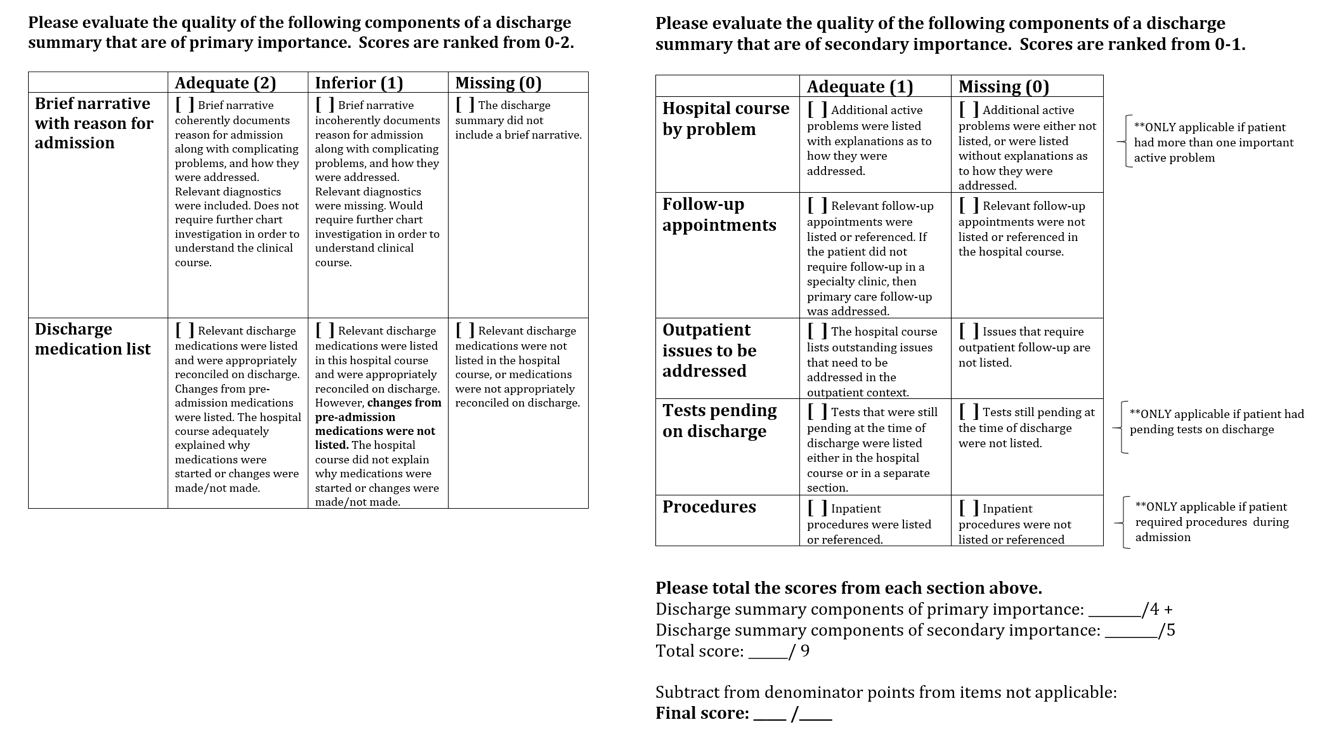
Description: The first stage of the project involved surveying primary care attending physicians among two of the three healthcare networks associated with the Tulane University Department of Medicine, including Tulane Internal Medicine residents themselves, who also serve in primary care roles. The next step was to develop an evaluation tool based on these survey results as well as a review of the literature. An intervention was developed to improve resident discharge summaries using this tool as a guide and conducted over a five-week period. Pre- and post-intervention discharge summaries are currently being evaluated with the tool to assess for significant differences.
Conclusions: The initial surveys identified the two most important components of discharge summaries as: 1) a brief narrative with a reason for admission, and 2) an accurate discharge medication list. The next most highly emphasized components consisted of: 1) a hospital course by problem, 2) a list of follow-up appointments, 3) outpatient issues to be addressed, 4) tests pending at discharge, and 5) procedures performed while inpatient. This was consistent with a literature review. Overall, the surveys rated the resident discharge summaries as fair to good. An evaluation tool was created weighting the two highest-ranked components greater than the following five components. The intervention involved reviewing the results of the surveys with the residents, discussing the evaluation tool, and having residents practice using the tool to evaluate sample discharge summaries with a partner. Whether this workshop will improve the quality of resident discharge summaries has yet to be seen once the pre- and post-intervention evaluations are complete.