Background: During the COVID19 pandemic, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and US Department of Health and Human Services liberalized guidelines to allow for broader access to telehealth services. Previously the use of telehealth platforms in hospital and by the hospitalists has been limited.
Purpose: Describe rapid implementation of an interprofessional, inpatient, secure telehealth platform that maintain our commitment to patient centered care and has capacity to limit team exposure to COVID-19 with potential conservation of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
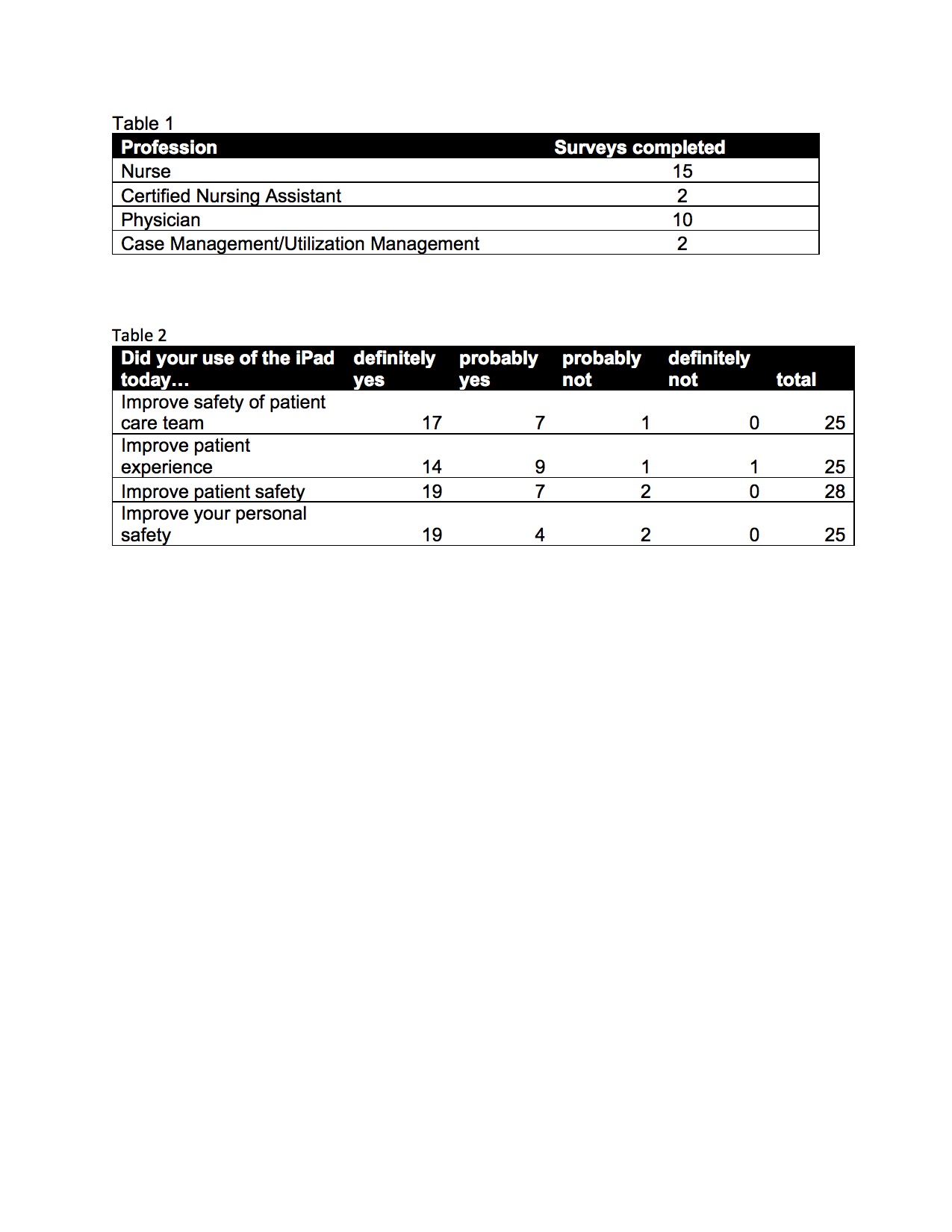
Description: In March 2020 we implemented use of a telehealth platform on a dedicated COVID-19 unit at Duke Regional Hospital using Cisco Jabber on iPads. iPads were placed in PUI/COVID-19 patient rooms and the nursing station. Best practice guidelines on national organization recommendations and technical instructions were available at the point of care and were also sent via email to potential users. Video assisted calls also allowed visualization of patients in closed door rooms and family video visitation during a time of visitor restrictions. To assess user experience at the pilot site, a survey accessible via QR code or link was placed by the iPads. 29 surveys were completed (Table 1). The survey asked about ease of use, improvements in safety, patient experience and PPE usage (Table 2). 76% of respondents were able to complete their patient encounter without use of PPE. Open ended questions were included to generate areas for iterative improvement in the telehealth project.We quickly expanded from our initial pilot site to other health system sites. From March 2020 to May 2020, team member-initiated calls using the telehealth platform ranged from 2062 to 4980 per month within our health system, potentially saving an estimated 11947 PPE bundles representing a potential cost savings of $29,270.15.
Conclusions: Inpatient telehealth use by hospital medicine teams has the potential to conserve PPE. User responses also suggest positive impacts on safety and patient experience. Future directions include improving user experience and incorporating wireless exam devices such as stethoscopes to broaden the potential applications for inpatient telehealth.