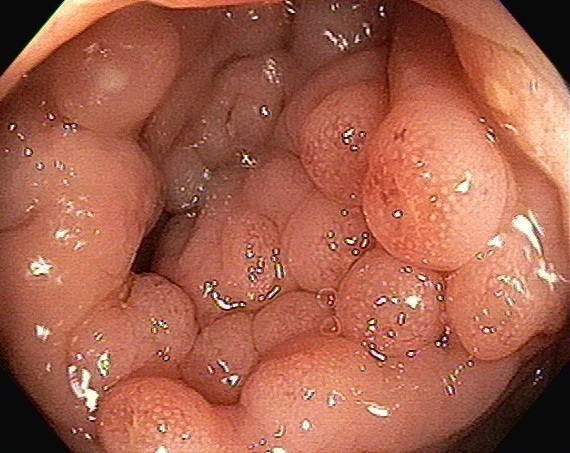
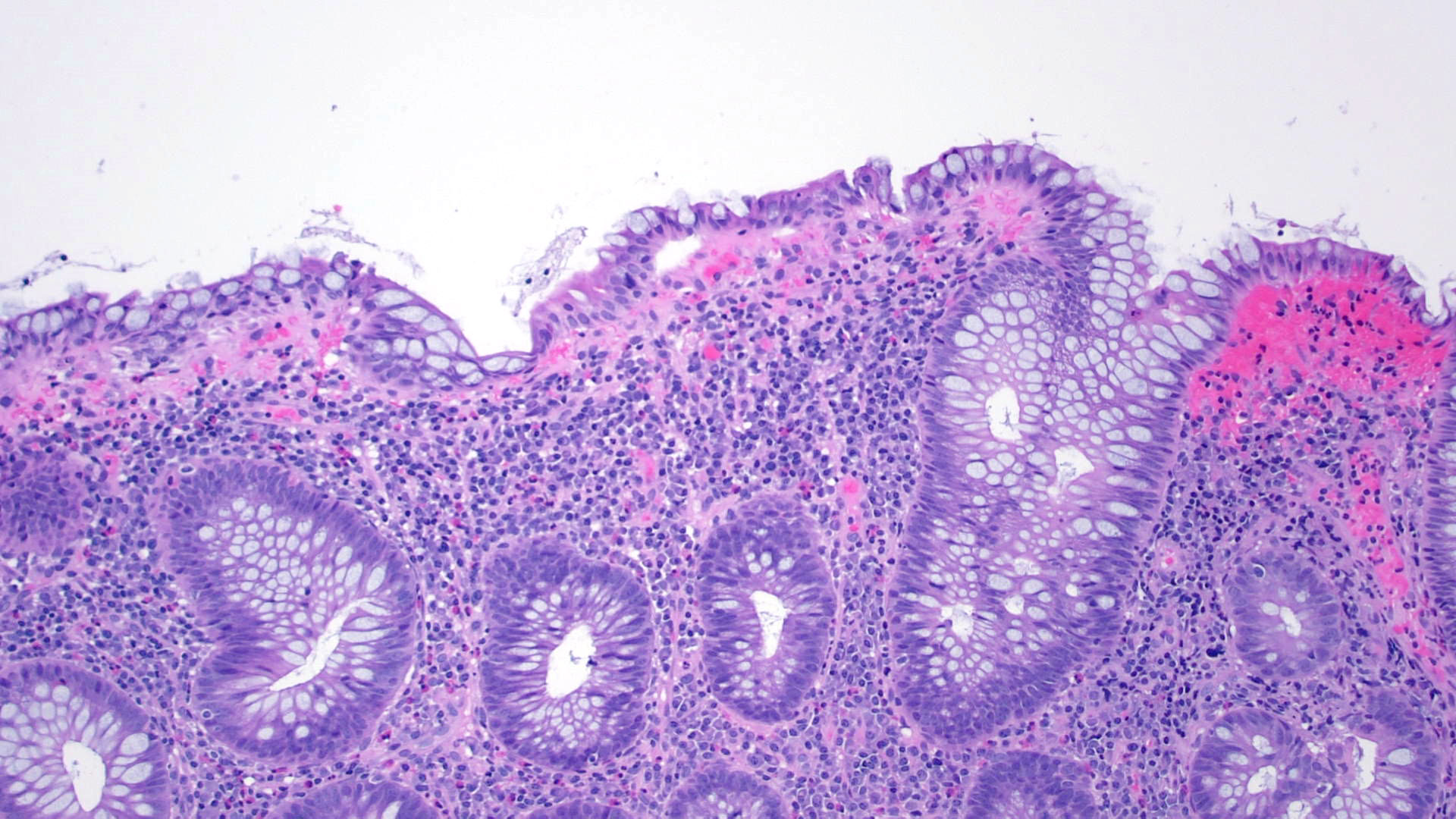
Case Presentation: 25 year-old female with past medical history of irritable bowel syndrome and asthma was evaluated for one year of watery diarrhea. She reported 3-4 watery bowel movement daily associated with abdominal cramping. No blood reported in the stool. No changes in weight or appetite reported. No fever or chills. She reported symptoms started after a course of antibiotics for URI a year back. Physical exam including vital signs on presentation were unremarkable. Serum chemistries including liver enzymes were unremarkable. Stool culture, ova and parasites were unremarkable. Stool Clostridium difficile was also negative. Stool occult was positive. She was screened for celiac disease and IBD but negative for tissues transglutaminase, anti-endomysial and saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies. Patient underwent colonoscopy for the evaluation of chronic diarrhea and revealed multiple polyps throughout the colon with inflamed surface which were biopsied. Concern was for hyperplastic polyposis syndrome. Genetic testing for APC gene was done and came back negative. Biopsy from polyps revealed lymphocytic colitis. Patient was started on budesonide with marked improvement in her symptoms.
Discussion: Lymphocytic colitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of colon usually presented in young to middle age female as watery diarrhea. The estimated incidence of lymphocytic colitis is about 3 per 100,000. Chronic non bloody diarrhea with or without abdominal pain is a most common presentation. Smoking and use of NSAIDS are associated with increased risk. A colonoscopy with mucosal biopsy is necessary to establish the diagnosis of lymphocytic colitis as severity of diarrhea usually correlates with the inflammatory changes seen in the lamina propria. Colonoscopy usually revealed normal appearing mucosa. Our patient had an atypical endoscopic finding which mimic hyperplastic polyposis syndrome which is rare condition characterized by multiple, large and/or proximal serrated polyps. Patient with active disease benefit from budesonide therapy. Combination of cholestyramine and lopearamide. Smoking cessation and avoidance of NSAIDS should be recommended.
Conclusions: Lymphocytic colitis is characterized by chronic non-bloody diarrhea in a young to middle age female. The diagnosis is usually made on biopsy on colonoscopy usually revealed normal appearing colonic mucosa. Our case highlighted an atypical endoscopic finding of this entity which mimic hyperplastic polyposis syndrome.