Background: The United States government has made decreasing 30-day unplanned readmissions a national priority, as early hospital readmissions are a common and costly occurrence. Establishment of the Hospital Readmission Reduction Program (HRRP) in 2012 led to financial penalties to hospitals with high 30-day readmission rates. As such, decreasing 30-day unplanned readmissions has become a key initiative at many institutions. Despite this, at our large, urban, academic medical center, 30-day unplanned readmissions increased on inpatient medicine units from 13.5% in FY2016 to 16.2% in FY2018.
Purpose: The purpose of our project was to decrease 30-day unplanned readmissions to inpatient medicine wards in a single, large, urban academic medical center.
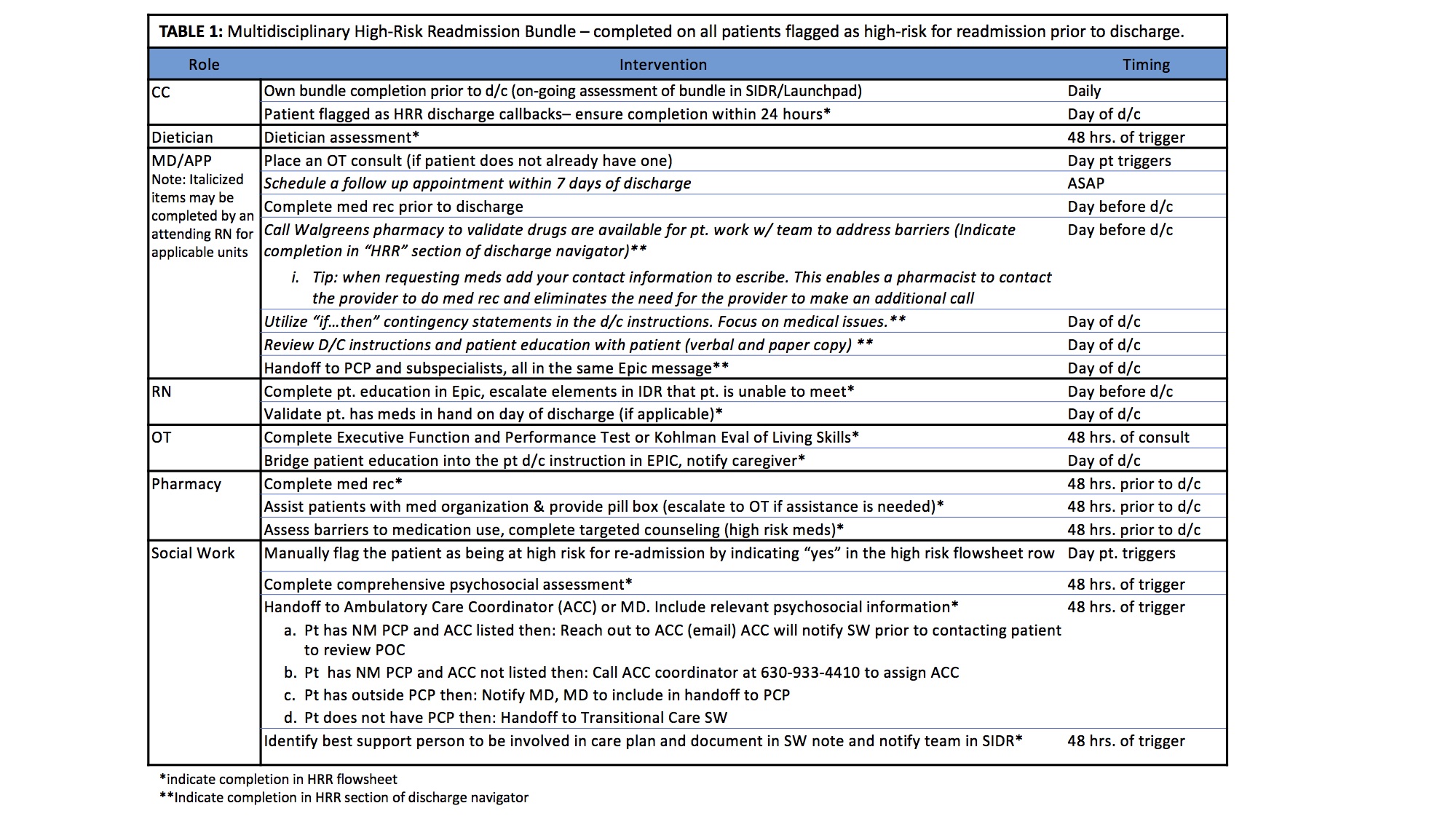
Description: Predictive modeling was used to identify specific drivers and associated coefficients tailored to our specific patient population to generate a “readmissions risk score”, which was available in the electronic medical record. A multidisciplinary task force was convened and a new process was implemented in two pilot units whereby a social worker flagged two patients per day as high-risk for readmission (HRR) based on their readmissions score. A multidisciplinary intervention bundle was completed on patients flagged as HRR prior to discharge (see Table 1). Each specialty (Charge Nurses, Dietician, MD/DO/APPs, RNs, Occupational Therapy, Pharmacy, and Social work) was assigned specific tasks to complete prior to discharge for flagged patients. Unplanned readmissions within 30 days were then monitored in two pilot units and five control units over four months.
Conclusions: Between 4/1/2019 and 7/31/2019, use of the Risk Stratification Model and completion of the High-Risk Readmission Bundle resulted in a decreased rate of 30-day unplanned readmissions by 1% and 2.5% in our two pilot units, while the other five control units all had consistent increases in 30-day readmissions by 1%. Our data demonstrates that a group of targeted interventions can successfully decrease readmissions of patients identified as high-risk for readmission using predictive modeling.