Background: SGLT-2 inhibitors are one of the emerging drugs in heart failure. Several meta-analyses prove its effect in reducing the composite outcome of cardiovascular death/hospitalization for heart failure but it is unknown if they contain all the primary studies hence a need for a pooled analysis
Methods: We performed an umbrella analysis and used the AMSTAR 2 tool to qualify systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Inverse variance method was used in Revman software.
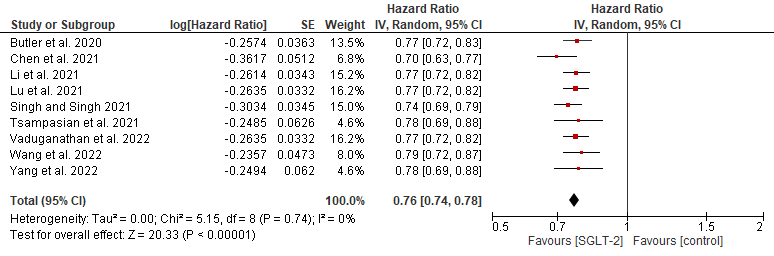
Results: In this analysis, a total of 9 reviews were included. There was overlap in primary studies but none of them had all the primary studies. Pooled analysis found that cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure among heart failure patients was significantly reduced with actual reductions ranging between 21% and 30% when SGLT-2 inhibitors are used compared with control. Pooled results from this study also found that SGLT-2 inhibitors significantly reduced the risk of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure among heart failure patients by 24% compared to Control, HR 0.76; 95% CI, 0.74-0.78; p < 0.01; I2 = 0%).
Conclusions: SGLT-2i in heart failure can be considered to be of substantial benefit with regard to hospital outcomes of cardiovascular death/hospitalization.