Background: Goal-concordant care is an ongoing challenge in hospital settings. Failures in communication with patients and caregivers can lead to unwanted usage of hospital resources, including the ICU. This leads to lower quality care for patients and increased burden on the hospital. Goals of care conversations can be utilized to ensure that care aligns with patients’ priorities and values. Through the use of a novel machine learning algorithm, we were able to generate highly accurate mortality predictions using EHR data.1,2 The mortality risk score generated by the machine learning algorithm was able to call attention to the serious illness conversation needs of patients with a high mortality risk within 30 days.
Purpose: To improve rates of advanced care planning (ACP) notes in both academic and community hospitals for patients with a high mortality risk within 30 days and reduce the utilization of the ICU for those patients.
Description: Previously, key drivers in low utilization of ACP notes had been identified as limited clinician time and difficulty identifying appropriate patients.3 Through the implementation of the machine learning algorithm, we were able to ease the burden of both of these issues. This intervention for increasing goal-concordant care was tested in both an academic and community hospital setting. Through the use of our machine learning algorithm, adult patients with a high risk of 30-day mortality were identified. Upon identification of a high risk of mortality within 30 days, hospitalists were notified of the computed high risk mortality score and prompted to hold goals of care conversation. Compliance with the automated ACP note request was voluntary.
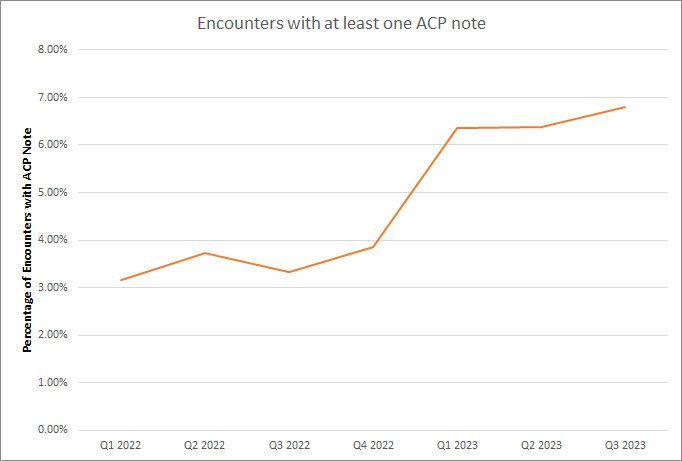
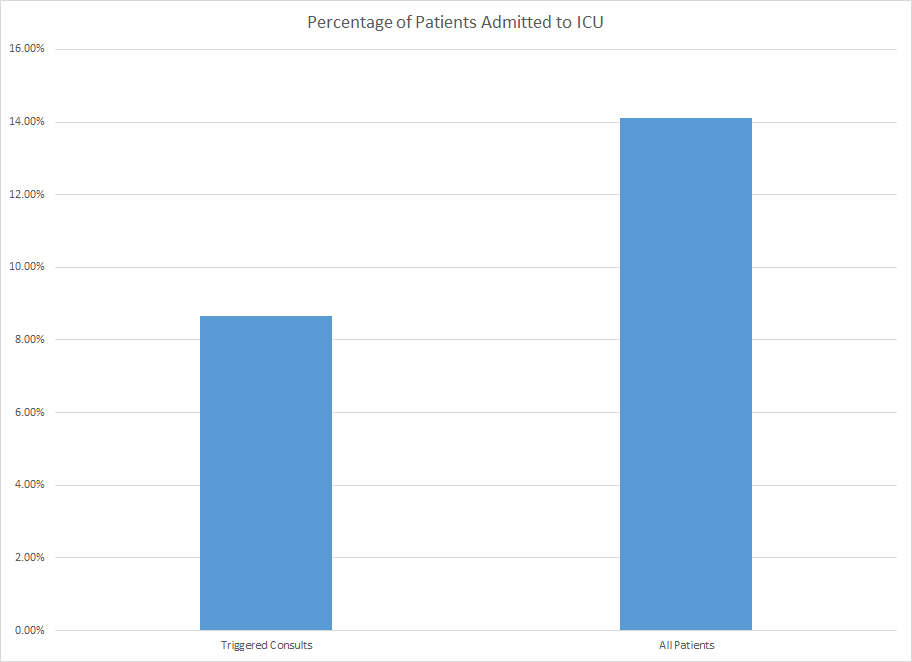
Conclusions: Our preliminary data shows that by utilizing a novel machine learning algorithm and provider notification in the electronic medical record, we were able to increase the percentage of inpatient admissions with at least one ACP note from 3.15% in the first quarter of 2022 to 6.8% in the third quarter of 2023 across a quarterly average of 23,557 encounters. Additionally, in the first three quarters of 2023, preliminary data shows the percentage of patients receiving the intervention that were later admitted to the ICU was 8.65% versus a rate of 14.2% overall for the patient population at participating hospitals. Further analysis is needed to show the penetration of the intervention within the larger hospital system and its direct impact on the key stakeholder departments within each hospital.