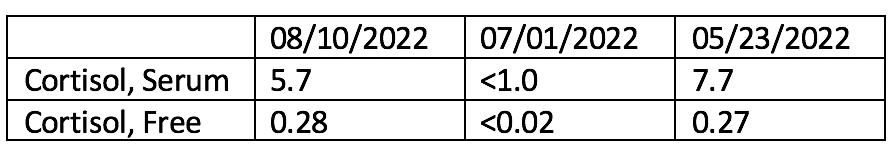
Case Presentation: A 63-year-old female with no prior oncologic history was found to have a right breast mass via ultrasound guided biopsy. Pathology showed invasive poorly differentiated metaplastic carcinoma triple negative breast cancer. She was started on neoadjuvant chemotherapy, including Keytruda (pembrolizumab) every 3 weeks. During therapy, she developed Grade 1 fatigue and anemia. Baseline thyroid function tests, liver functions tests, and cortisol levels were within normal limits. Baseline free cortisol level was 0.27 microg/ dL. One month after therapy, free cortisol level was < 0.02 microg/ dL. She had no other symptoms of immune mediated side effects or of adrenal insufficiency. During her initial visit prior to chemotherapy, she had reported use of vitamin C and D. She had been counseled on unknown interactions between vitamins and chemotherapy and immediately stopped the use of these vitamins. Further review of medications on follow up after her low cortisol levels revealed that she had added biotin supplementation, 10000 mcg per day for hair loss, which was ultimately held for the remainder of her treatment course.
Discussion: Although survival rates in many cancers have improved due to the development of anti- PD1 agents, immune related adverse effects (irAEs) can be introduced, which can be life threatening. Endocrine irAEs are some of the numerous AEs. Prevalence of adrenal insufficiency (AI) has been noted to be < 2% [1,3,4]. Symptoms include headache, anorexia, fatigue, nausea, all of which are nonspecific. When the morning cortisol is < 250nmol/L or the random cortisol is < 150nmol/ L, ACTH levels are obtained, along with initiation of glucocorticoid therapy [1,2,3]. Major steps are taken to diagnose and treat irAEs, and treatment with lifesaving chemotherapy is interrupted due to the concern of development of side effects from anti PD1 agents.Along with the knowledge and surveillance of irAEs, clinicians must consider all causes of a patient’s clinical presentation. In our case, the patient reported addition of biotin supplements after neoadjuvant treatment was started. There have been several reports of biotin interference with testing for multiple tests [5,6] Prior studies have shown that biotin interference with “competitive immunoassays can cause falsely increased results, whereas biotin interference with immunometric ‘sandwich’ assays falsely lowers results” [6,7]. Unfortunately, these false labs and misinterpretations lead to misdiagnosis, stress, unnecessary procedures, and cessation of lifesaving treatment. In our case, our patient was found to have low cortisol levels, without any clear symptoms of adrenal insufficiency. Obtaining a clear history, including all medications and OTC supplements was critical in understanding the cause of her lab results.
Conclusions: The patient’s cortisol level normalized off biotin supplements. The free cortisol after the patient was off biotin for 1 month was found to be 0.28 mcg/ dL. Dietary supplementation, as biotin, can lead to lab errors which presents risks to patient safety, leading to stress and unnecessary work up. In our case, there was concern for adrenal insufficiency leading to further workup. However, due to a thorough understanding of her history, her lifesaving chemotherapy was not terminated. Obtaining a full history, including medication list, along with non-prescription supplements is critical in appropriate treatment and prevention of misdiagnosis.