Background: Among patients undergoing cardiac surgery on cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), post-operative complications are common, occurring in up to 67% of patients, and significantly impact long-term outcomes. We conducted a Phase 2 clinical trial of RBT-1, a pharmacologic preconditioning drug, to assess cytoprotective biomarkers and clinical outcomes. Herein, we report our final results.
Methods: This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial enrolled 152 patients in the US, Canada, and Australia who were scheduled to undergo coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) and/or valve surgery on CPB. Eligible patients were randomized to receive one intravenous (IV) dose of RBT-1 (low or high dose) or placebo 24 to 48 hours before surgery. The primary endpoint was a cytoprotective preconditioning response, measured by a composite of biomarkers representing antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and iron scavenging pathways (ie, heme oxygenase-1 [HO-1], interleukin-10 [IL-10], and ferritin). Key secondary/exploratory endpoints included ventilator, intensive care unit (ICU), and hospital days; readmission rates; incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI) and major adverse kidney events (MAKE); and adverse events.
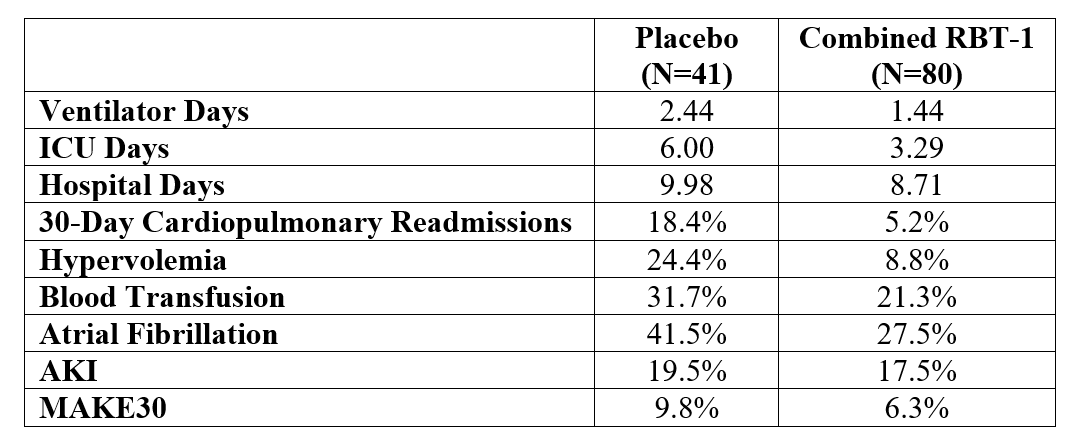
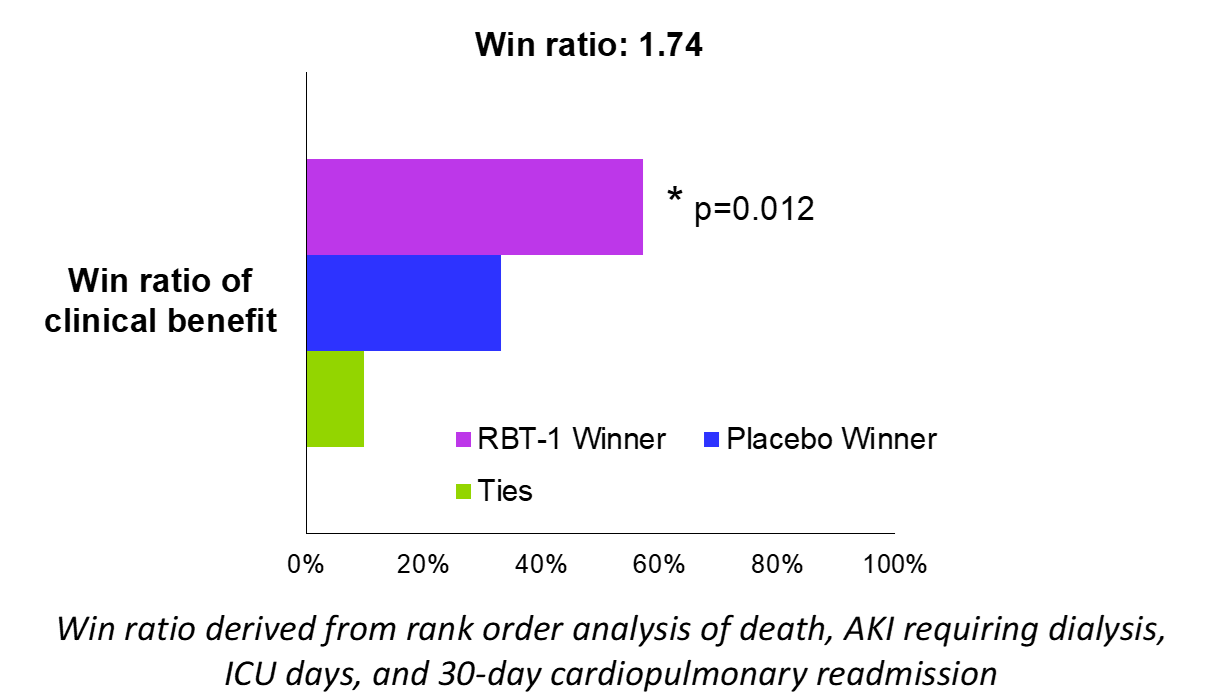
Results: Baseline characteristics were as follows: mean age, 65 years; heart failure, 15%; Stage 3 or 4 chronic kidney disease (CKD), 25%; and combined CABG/valve surgery, 23%. Both low and high doses of RBT-1 significantly increased the biomarker response by >160% (p< 0.0001), meeting the primary endpoint. RBT-1 yielded a significant reduction in ICU days (p=0.024), 30-day cardiopulmonary readmission rates (p=0.039), and hypervolemia (p=0.027), as well as a meaningful reduction in hospital days, blood transfusion, atrial fibrillation, and MAKE at Day 30 (MAKE30) (Table 1). RBT-1 was well tolerated with only transient photosensitivity (20% incidence) as the primary adverse event and more commonly seen in the high dose group. A post-hoc hierarchical composite (win ratio) of clinical outcomes (in rank-order of death, AKI requiring dialysis, ICU days, and 30-day cardiopulmonary readmission) achieved a statistically significant win ratio of 1.74 (p=0.012), suggesting RBT-1 improved clinical outcomes post-cardiac surgery (Figure 1).
Conclusions: RBT-1 is a novel preconditioning drug used safely in the setting of CABG/valve surgery requiring CPB. Treatment with RBT-1 resulted in favorable changes in cytoprotective biomarkers and suggested benefits on multiple clinical outcomes of relevance. Based on these findings, FDA has granted Breakthrough Therapy and Fast Track designation to advance clinical development of RBT-1 to reduce the risk of post-operative complications in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.