Background: Patient & Family Advisory Councils (PFACs) are groups of patients, family members and caregivers who meet regularly to share their experiences of healthcare or perspectives on a specific topic. Over 50% of acute care hospitals have PFACs. PFACs can also provide an opportunity to engage its members in research and quality improvement (QI) efforts, but this process has not been well defined. The aim of this study is to describe barriers to PFAC member engagement in inpatient research and QI efforts and strategies to support engagement in this context.
Methods: A team comprising of patient advisors, researchers, physicians and nurses were involved in all stages of this qualitative study. The study took place within the Hospital Medicine Re-Engineering Network (HOMERuN), a national Hospital Medicine collaborative that facilitates and conducts multi-center research to improve the outcomes of patients with acute illnesses. We invited PFAC members, PFAC leaders, hospital leaders, and hospitalist researchers from HOMERuN to participate in either a focus group or individual interview. Standardized questions were used to explore PFAC member engagement in research and QI. We used content analysis to analyze data.
Results: Eighty stakeholders (45 PFAC members, 12 PFAC leaders, 12 hospital leaders, 11 researchers) from 9 academic medical centers that are part of HOMERuN participated in 8 focus groups and 19 individual interviews.
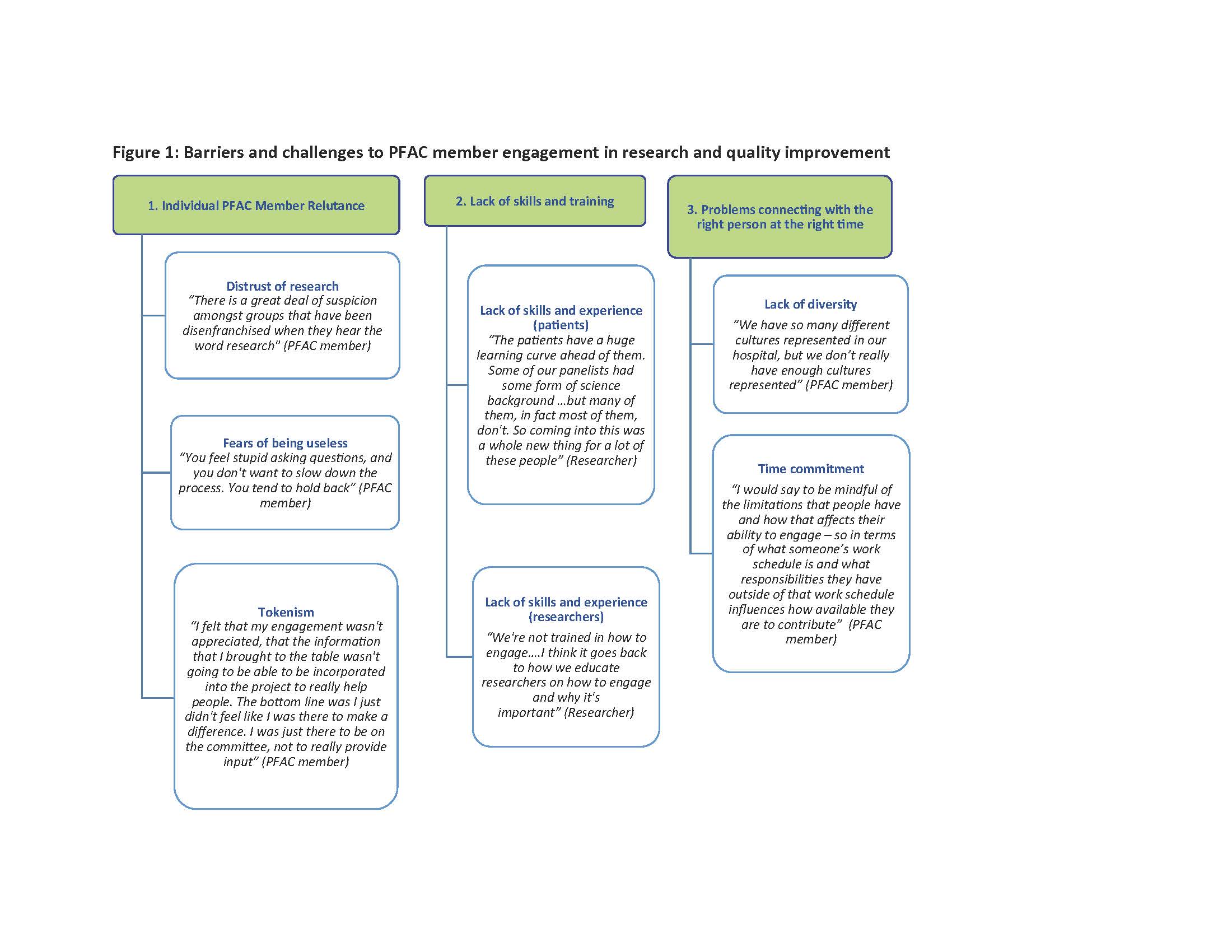
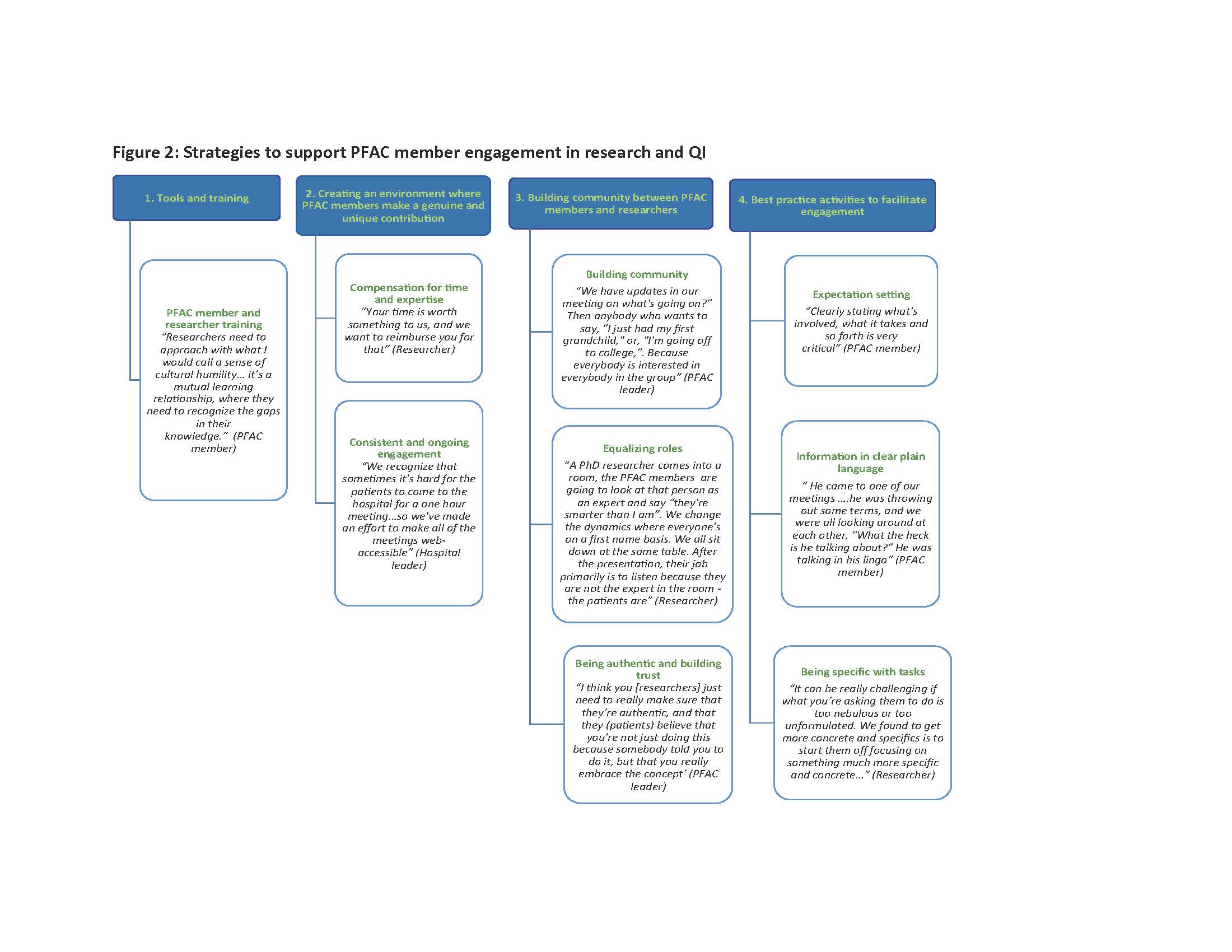
Barriers to PFAC member engagement in research and QI were organized into categories including; 1) individual PFAC member reluctance, 2) lack of skills and training for patients, caregivers, and researchers, 3) problems finding and connecting with PFAC members at the right time (Figure 1). Strategies to support PFAC member engagement in research and QI included; 1) tools and training 2) creating an environment where the PFAC members are making a unique contribution, 3) building community between PFAC members and researchers, 4) best practice activities to facilitate engagement (Figure 2).
Conclusions: Barriers to engaging PFAC members in research and QI relate to patients’ negative perceptions of research, logistical issues, and a lack of training for both patient and research stakeholders. Creating supportive environments to build community between PFAC members and researchers and QI experts are a foundation for effective partnerships. Our study has identified a number of shared training opportunities and activities for PFAC members and researchers to build skills that facilitate engagement in research and QI.