Background: By law, patients have prompt access to electronic discharge notes in their charts. Technical language and abbreviations make notes difficult to read and understand for a typical patient. Large language models such as GPT-4 may have the potential to transform these notes into patient-friendly language and format. Our objective was to determine whether GPT-4 can transform discharge summaries to be more readable and understandable.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study of patient discharge summaries. The study took place at NYU Langone Health. We included a sample from adult, general medicine patients discharged during the month of June 2023. Patients discharged as deceased were excluded. We used a secure HIPAA compliant platform, Microsoft Azure OpenAI, to transform these discharge summaries into a patient friendly format between July 26th and August 5th, 2023. Outcomes were readability as measured by Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level and understandability using PEMAT scores. We compared the readability and understandability of the original discharge summaries to the transformed, patient-friendly discharge summaries created through GPT-4. As balancing metrics, we measured accuracy and completeness using a novel survey instrument.
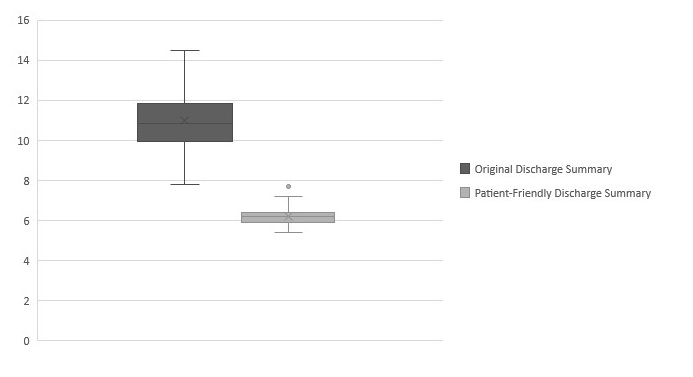
Results: A total of 50 patients were included. The median patient age was 65.5 years. Flesch-Kincaid Readability was suitable for significantly lower grade in the patient-friendly discharge summaries compared to the original discharge summaries (6.2 vs 11; p < 0.001). PEMAT understandability scores were significantly higher for patient-friendly discharge summaries, compared to original discharge summaries (81% vs 13%; p < 0.001). Two physicians reviewed each patient-friendly discharge summary for accuracy on a 6-point scale with 54% of (54/100) reviews giving the best possible rating. Summaries were rated entirely complete in 56% of reviews (56/100). 18 reviews noted safety concerns.
Conclusions: In this cross-sectional study of 50 patient discharge summaries we showed that GPT-4 can be used to transform discharge summaries into patient-friendly language and format that is significantly more readable and understandable than discharge summaries as they appear in electronic health records. However, implementation will require improvements in accuracy, completeness, and safety. Given the safety concerns initial implementation will require physician review.