Background: Hepcidin-25 is a liver-derived peptide hormone that regulates iron homeostasis in humans. Recent studies have suggested that it also plays a key role in host-pathogen interface. Iron is essential for the survival and growth of bacteria. When the bacteria infect macrophages, macrophages release a number of cytokines, including interleukin-6, which induce hepatic production of hepcidin-25. This hepcidin up-regulation leads to iron depletion and inhibition of bacterial growth. The aim of this study is to investigate time course of serum hepcidin-25 levels and ferrokinetic parameters in patients with bacteremia.
Methods: Of all patients who were admitted to our department because of suspected bacterial infection between August 1, 2015 and March 31, 2018, 30 consecutive patients (aged 69±17, male 10, female 20) with positive blood cultures were enrolled. We measured complete blood cell count, hepcidin-25, iron, iron-binding capacity, ferritin, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, albumin, and C-reactive protein at day 1, 2, 3 and 7 after admission.
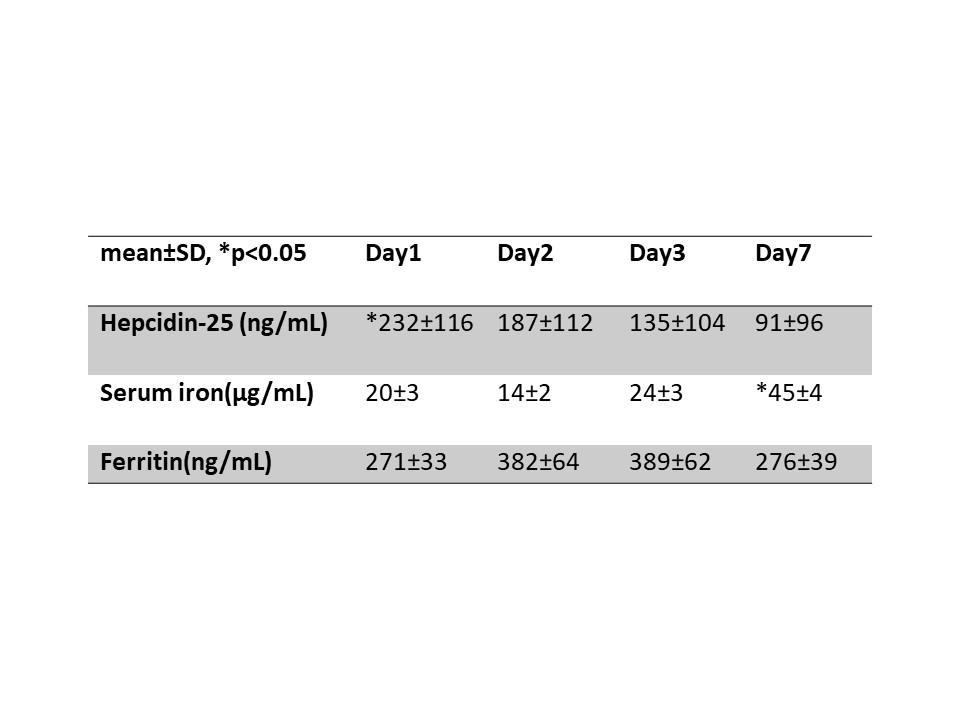
Results: Pathogens detected by blood cultures were Esherichia coli (n=16), β-streptococcus (n=5), Klebsiella pneumonia (n=2), Enterococcus faecalis (n=2), Proteus mirabillis (n=1), Staphylococcus aureus (n=1), MRSA (n=1), Streptococcus anginosus (n=1), Enterobactor cloacae (n=1), GNR (n=1). Hepcidin-25 levels on day1 were highest and decreased significantly during hospital days (day1 232±116 ng/ml, day2 187±112 ng/ml, day3 135±104 ng/ml, day7 91±96 ng/ml P<0.05). Serum iron levels on day1, 2, and 3 were significantly lower than on day 7 (day1 20±3 µg/dl, day2 14±2 µg/dl, day3 24±3 µg/dl, day7 45±4 µg/dl P<0.05). Differences in serum ferritin levels within each day were not significant (day1 271±33 ng/ml, day2 382±64 ng/ml, day3 389±62 ng/ml, day7 276±39 ng/ml).
Conclusions: Our study suggests that upregulation of hepcidin-25 occurs in the very early stage of bacteremia and is associated with hypoferremia during 3 days after admission.